Virtual private cloud (VPC) is a transformative cloud networking solution that offers a plethora of benefits and applications. By creating a private, isolated network within a public cloud, VPCs provide businesses with enhanced security, flexibility, and control over their network infrastructure.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of VPCs, exploring their key components, configuration options, connectivity methods, and security measures. We will also delve into the various use cases and applications of VPCs, showcasing how they can empower businesses across diverse industries.
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) Definition and Concepts
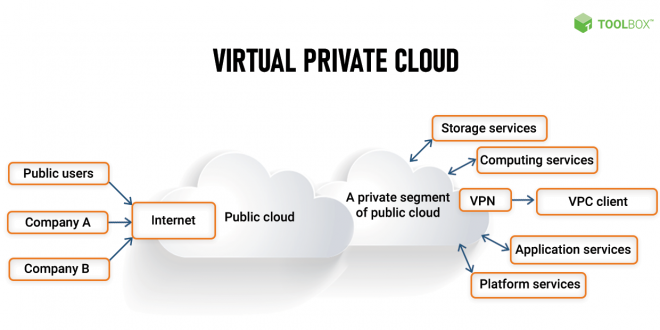
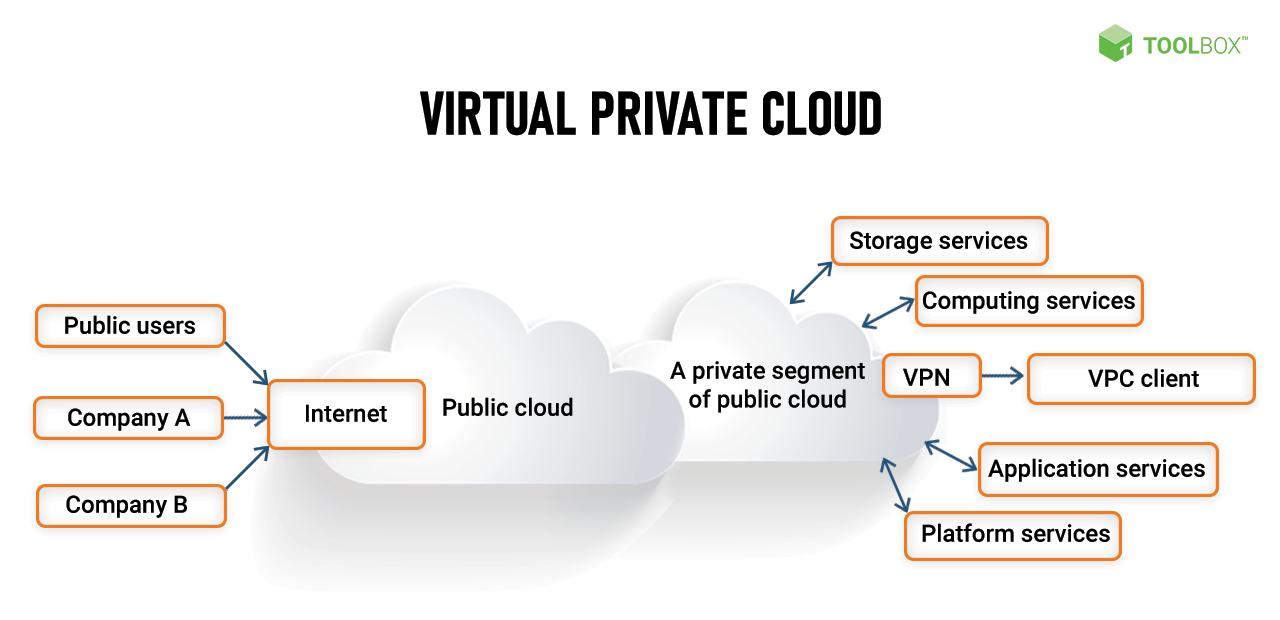
A Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a virtual network that provides a secure and isolated environment for your resources in the cloud. It allows you to create a private network that is isolated from the public internet and other VPCs, giving you more control over your network traffic and security.
The key components of a VPC include:
- VPC network:The virtual network that you create within a region.
- Subnets:Subdivisions of the VPC network that you can use to group resources.
- Network gateways:Devices that allow you to connect your VPC to other networks, such as the public internet or on-premises networks.
- Security groups:Firewalls that you can use to control traffic within and between VPCs.
- Route tables:Tables that determine how traffic is routed within and between VPCs.
VPCs offer several benefits, including:
- Improved security:VPCs provide a secure and isolated environment for your resources, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Increased control:VPCs give you more control over your network traffic and security, allowing you to customize your network to meet your specific needs.
- Scalability:VPCs can be easily scaled to meet your changing needs, allowing you to add or remove resources as needed.
- Cost-effectiveness:VPCs can be a cost-effective way to create a private network in the cloud, as you only pay for the resources that you use.
Types of VPCs
Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) are customizable, isolated network environments within the Google Cloud Platform (GCP). VPCs provide a secure and scalable way to connect and manage resources within a project. There are several types of VPCs available, each with its own set of features and use cases.
Regional VPCs
Regional VPCs span a single region and provide a way to connect resources within that region. Regional VPCs are ideal for applications that require low latency and high throughput within a specific region. For example, a regional VPC could be used to host a website or application that is targeted at users in a particular region.
Multi-regional VPCs, Virtual private cloud
Multi-regional VPCs span multiple regions within a single continent. Multi-regional VPCs are ideal for applications that require high availability and low latency across multiple regions. For example, a multi-regional VPC could be used to host a website or application that is targeted at users in multiple countries within a continent.
Global VPCs
Global VPCs span all regions and provide a way to connect resources across the globe. Global VPCs are ideal for applications that require high availability and low latency across multiple continents. For example, a global VPC could be used to host a website or application that is targeted at users all over the world.
VPC Configuration and Management
VPC configuration involves creating and customizing a virtual private cloud to meet specific network and security requirements. It includes defining the VPC’s network range, subnet structure, and routing configuration.
Effective VPC management encompasses monitoring, troubleshooting, and optimizing network performance, as well as implementing security measures to protect against unauthorized access.
Creating and Configuring a VPC
- Choose a region and availability zones for the VPC.
- Define the VPC’s IP address range (CIDR block).
- Create subnets within the VPC to segment the network logically.
- Configure routing tables to control traffic flow between subnets and the internet.
- Enable network access control lists (ACLs) to restrict traffic based on source and destination IP addresses.
VPC Configuration Settings
- Network Range:The IP address range (CIDR block) assigned to the VPC.
- Subnet Structure:The division of the VPC into smaller logical segments called subnets.
- Routing Configuration:The rules that determine how traffic is routed within and outside the VPC.
- Security Groups:Firewall rules that control access to resources within the VPC.
- Network ACLs:Firewall rules that control traffic flow between subnets.
Best Practices for VPC Management
- Use a hierarchical subnet structure to organize and isolate network segments.
- Implement least-privilege access control to restrict access to resources.
- Monitor network traffic and performance regularly to identify and address issues.
- Automate VPC management tasks to reduce manual errors and improve efficiency.
- Stay up-to-date with VPC best practices and security recommendations.
VPC Connectivity and Security
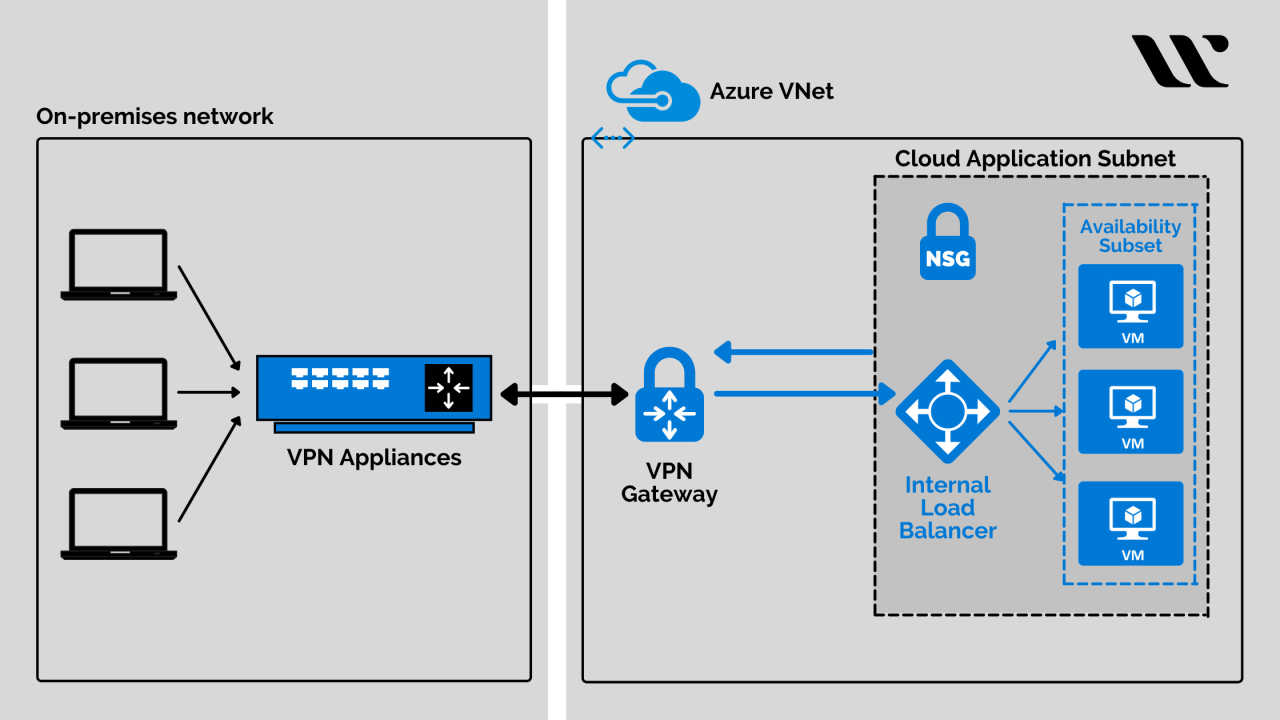
Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) provide secure and isolated network environments within the cloud. Understanding how to connect to and within a VPC, as well as the security measures available, is crucial for effective VPC management.
VPCs offer various connectivity options, including:
- Private connectivity:VPCs can be connected to on-premises networks using VPNs or dedicated connections, allowing secure data transfer between private networks and the cloud.
- Public connectivity:VPCs can be connected to the public internet via gateways, enabling access to public resources and services.
- Inter-VPC connectivity:VPCs can be peered with other VPCs within the same project or across projects, allowing resources in different VPCs to communicate directly.
Security Measures for VPCs
VPCs offer robust security measures to protect data and resources within the cloud:
- Network segmentation:VPCs create isolated network environments, separating resources from the public internet and other VPCs, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Firewall rules:VPCs allow administrators to define firewall rules to control inbound and outbound traffic, filtering out malicious or unauthorized access attempts.
- Access control lists (ACLs):ACLs define the rules for network traffic within a VPC, specifying which resources can communicate with each other.
- Security groups:Security groups are applied to individual instances within a VPC, allowing administrators to define granular access controls for each instance.
- Network logging:VPCs provide logging capabilities to monitor network traffic and identify potential security threats.
Role of VPCs in Network Security
VPCs play a vital role in enhancing network security by:
- Isolation:VPCs isolate resources from external threats, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
- Control:VPCs provide administrators with granular control over network traffic, allowing them to define specific access rules and security policies.
- Monitoring:VPCs offer logging and monitoring capabilities, enabling administrators to track network activity and identify potential security risks.
VPC Use Cases and Applications: Virtual Private Cloud
Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) offer a wide range of use cases and applications, enabling businesses to securely and efficiently manage their network resources in the cloud. Here are some common scenarios where VPCs are utilized:
VPCs provide a secure and isolated network environment within a public cloud platform, allowing organizations to create and manage their own private networks. This enables them to control network configurations, security policies, and routing, ensuring data privacy and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Benefits of VPCs for Specific Use Cases
- Hosting Private Applications:VPCs allow businesses to host private applications within the cloud while maintaining control over network access and security. This is particularly beneficial for applications that handle sensitive data or require specific network configurations.
- Cloud Migration:VPCs facilitate the migration of on-premises applications and workloads to the cloud by providing a seamless and secure transition. Businesses can create VPCs that mirror their existing network infrastructure, ensuring a smooth and controlled migration process.
- Hybrid Cloud Connectivity:VPCs enable organizations to establish secure and private connections between their on-premises networks and cloud resources. This allows for the integration of cloud services with existing IT infrastructure, providing flexibility and scalability.
- Multi-Tenant Environments:VPCs can be used to create isolated and secure environments for multiple tenants within a single cloud platform. This enables service providers to offer tailored cloud services to their customers while maintaining data privacy and security.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, VPCs have emerged as a cornerstone of modern cloud networking, providing organizations with a secure and scalable solution to meet their evolving network requirements. By leveraging the capabilities of VPCs, businesses can optimize their network infrastructure, enhance security, and drive innovation.
 Bussines News Daily
Bussines News Daily