Private cloud, an exclusive computing environment tailored to specific organizations, offers a compelling blend of security, performance, and cost optimization. As the demand for data protection and operational efficiency surges, private cloud emerges as a transformative solution, redefining the way businesses manage their IT infrastructure.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of private cloud, exploring its key characteristics, benefits, and use cases. We also examine the infrastructure components, security considerations, and challenges associated with managing a private cloud environment. Furthermore, we shed light on the latest trends and advancements, providing valuable insights into the future of private cloud technology.
Definition and Overview of Private Cloud
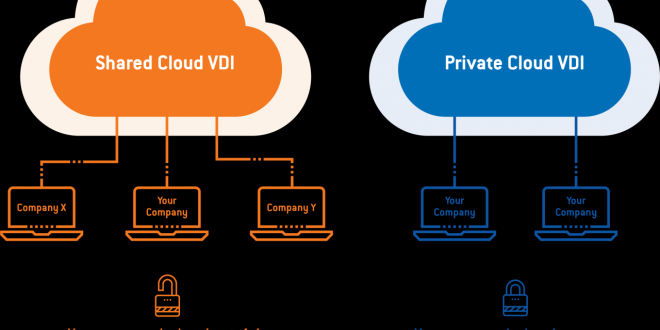
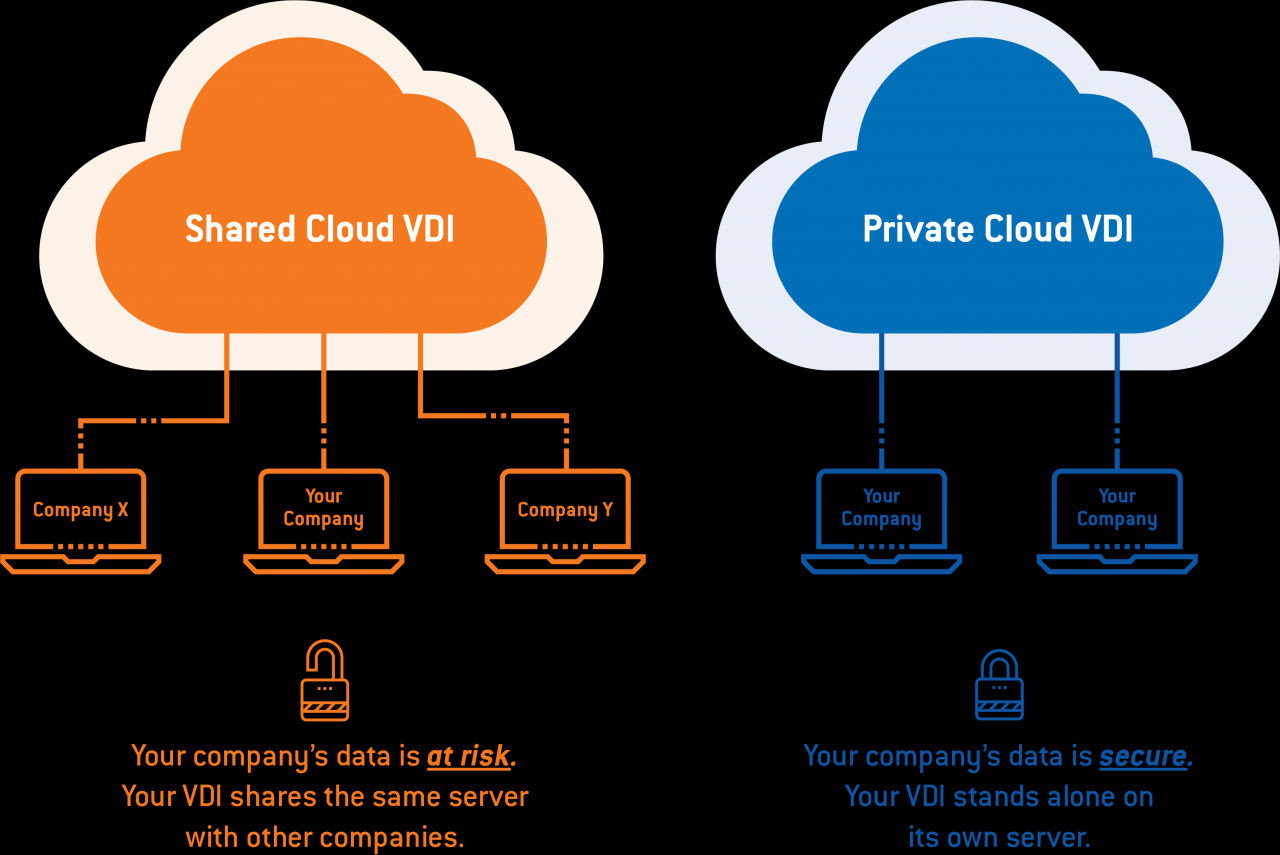
A private cloud is a cloud computing model that provides dedicated cloud services to a single organization. It offers a secure and isolated environment for organizations to host and manage their applications and data, ensuring greater control, customization, and compliance.
Unlike public clouds, which share resources among multiple tenants, private clouds are exclusively dedicated to a single organization. This provides several advantages, including enhanced security, performance, and flexibility. Private clouds offer a high degree of customization and control, allowing organizations to tailor their cloud environment to their specific needs and requirements.
Differences Between Private Cloud and Other Cloud Models
Private clouds differ from other cloud models in several key aspects:
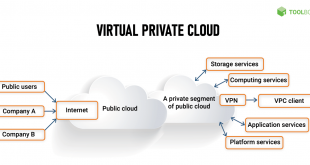
- Public Cloud:Public clouds are shared, multi-tenant environments where resources are pooled and allocated dynamically. They offer low cost, scalability, and accessibility, but may not provide the same level of security, control, or customization as private clouds.
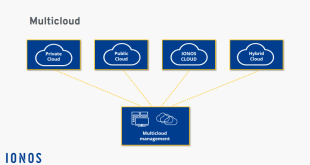
- Hybrid Cloud:Hybrid clouds combine elements of both private and public clouds. They provide organizations with the flexibility to allocate workloads between private and public cloud environments based on specific requirements. Hybrid clouds offer a balance of security, control, and cost-effectiveness.
Benefits of Private Cloud
Private clouds offer numerous advantages that make them an attractive option for businesses seeking to enhance their IT infrastructure.
These benefits include:
Enhanced Security and Data Control
- Private clouds provide enhanced security measures, as they are isolated from public networks and accessible only to authorized users.
- Businesses have complete control over their data and can implement custom security policies to meet their specific compliance requirements.
Improved Performance and Reliability
- Private clouds offer dedicated resources, ensuring consistent performance and high availability.
- Businesses can customize their cloud environment to meet their specific workload demands, optimizing performance and minimizing downtime.
Reduced Costs
- Private clouds can reduce costs compared to public clouds, as businesses only pay for the resources they consume.
- Eliminating the need for on-premises infrastructure can also lead to significant savings in hardware, maintenance, and energy costs.
Use Cases of Private Cloud
Private clouds offer a range of use cases that cater to the unique requirements of various industries. They provide secure and flexible infrastructure for hosting sensitive data, running mission-critical applications, and delivering cloud-based services.
Organizations across diverse sectors are leveraging private clouds to enhance their operations and gain a competitive edge.
Hosting Sensitive Data
Private clouds are ideal for storing and managing sensitive data that requires stringent security measures. They provide complete control over data access and protection, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards.
- Financial institutions use private clouds to safeguard customer data, including account information, transactions, and credit scores.
- Healthcare organizations rely on private clouds to securely store patient medical records, ensuring privacy and compliance with HIPAA regulations.
Running Mission-Critical Applications
Private clouds provide a reliable and high-performance environment for running mission-critical applications that are essential for business operations.
- Manufacturing companies use private clouds to host enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems that manage supply chain, inventory, and production processes.
- Telecommunications providers rely on private clouds to run core network infrastructure, ensuring uninterrupted service delivery to customers.
Providing Cloud-Based Infrastructure
Private clouds can be used to provide cloud-based infrastructure as a service (IaaS) to internal departments or external customers.
- IT departments can use private clouds to offer self-service cloud resources to developers and business units, enabling them to provision and manage their own infrastructure.
- Service providers can offer private cloud services to customers who require a dedicated and secure cloud environment for their applications and data.
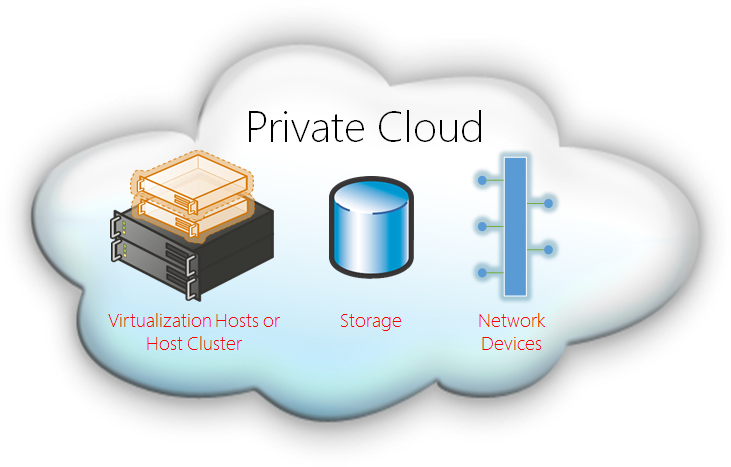
Components of Private Cloud Infrastructure
A private cloud infrastructure comprises various components that work together to provide a secure and dedicated computing environment. These components can be categorized into four main groups:
- Compute
- Storage
- Network
- Management Tools
Compute
The compute component consists of physical servers and virtual machines (VMs) that provide the processing power for running applications and workloads.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Servers | Physical machines that host virtual machines and provide computing resources. |
| Virtual Machines (VMs) | Virtualized computing environments that run on physical servers, providing isolation and flexibility. |
Security Considerations for Private Cloud
Private cloud environments require robust security measures to protect data, applications, and infrastructure. This section Artikels the key security considerations and best practices for private cloud deployments.
The security of a private cloud is paramount, as it hosts sensitive data and applications. It is crucial to implement a comprehensive security strategy that encompasses access control, data encryption, and vulnerability management to safeguard the cloud environment.
Access Control and Authentication
Access control and authentication are essential for controlling who can access the private cloud and its resources. Implementing strong access controls helps prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC):RBAC assigns permissions based on roles, ensuring that users only have access to the resources they need.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):MFA requires users to provide multiple forms of identification, such as a password and a one-time code, to access the cloud.
- Single Sign-On (SSO):SSO allows users to access multiple applications with a single set of credentials, reducing the risk of password fatigue and credential theft.
Data Encryption and Protection, Private cloud
Data encryption is vital for protecting sensitive data stored in the private cloud. Encryption techniques ensure that data remains confidential, even if it is intercepted or accessed by unauthorized individuals.
- Encryption at Rest:Encrypts data stored on physical storage devices, such as hard drives and solid-state drives.
- Encryption in Transit:Encrypts data while it is being transmitted over the network, preventing eavesdropping and data interception.
- Key Management:Implements secure key management practices, including key rotation and encryption key storage.
Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating vulnerabilities in the private cloud infrastructure. Regular vulnerability scans and patching help prevent attackers from exploiting vulnerabilities and gaining unauthorized access.
- Vulnerability Scanning:Regularly scans the cloud infrastructure for vulnerabilities, including software, operating systems, and network configurations.
- Patch Management:Applies security patches to address vulnerabilities and close security holes.
- Security Monitoring:Monitors the cloud environment for suspicious activities and security events, enabling prompt detection and response to potential threats.
Challenges of Private Cloud
The implementation and management of a private cloud can present various challenges for organizations.
High Upfront Costs
Private clouds require significant initial investments in hardware, software, and infrastructure, which can be a financial burden for organizations with limited budgets.
Complexity and Technical Expertise Required
Managing a private cloud requires specialized technical expertise and knowledge. Organizations may need to hire or train qualified personnel to operate and maintain the cloud environment.
Integration with Existing Infrastructure
Integrating a private cloud with existing IT systems and infrastructure can be complex and time-consuming. Organizations need to ensure compatibility and interoperability between the private cloud and their legacy systems.
Trends and Future of Private Cloud
The future of private cloud computing is bright, with continuous advancements and innovations shaping its landscape. As businesses seek greater control, flexibility, and security for their IT infrastructure, private cloud solutions are poised to play a pivotal role.
Emerging trends in private cloud technology include the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) for enhanced automation, optimization, and predictive analytics. Hybrid cloud models are also gaining traction, enabling businesses to seamlessly combine private and public cloud environments for optimal resource utilization and cost efficiency.
Emerging Use Cases and Innovations
Private cloud technology is finding applications in various industries and use cases. Healthcare organizations are leveraging private clouds for secure storage and management of sensitive patient data, while financial institutions are utilizing them for compliance and regulatory adherence. Additionally, private clouds are enabling innovative applications such as edge computing, IoT device management, and data analytics at scale.
Last Recap
Private cloud has revolutionized the IT landscape, empowering organizations with unprecedented control over their data and applications. Its customizable nature and robust security features make it an ideal choice for businesses seeking to enhance their security posture, improve performance, and optimize costs.
As technology continues to evolve, private cloud will undoubtedly play an increasingly pivotal role in shaping the future of enterprise computing.
 Bussines News Daily
Bussines News Daily