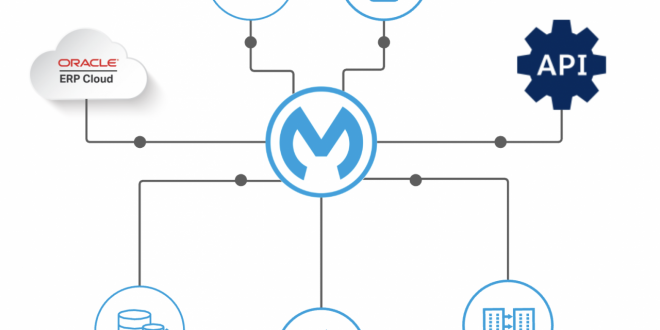
Oracle ERP integration unlocks a world of possibilities, empowering businesses to seamlessly connect their systems and unlock the full potential of their enterprise resource planning (ERP) solutions. This transformative approach offers a plethora of benefits, ranging from enhanced data accuracy and streamlined operations to improved decision-making and increased productivity.
Delving into the realm of Oracle ERP integration, we will explore the various methods and best practices for successful implementation, ensuring that your organization leverages this powerful tool to its fullest potential.
Oracle ERP Integration Overview
Oracle ERP integration involves connecting Oracle Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems with other software applications to streamline business processes, improve data accuracy, and enhance operational efficiency.
By integrating Oracle ERP with other systems, organizations can:
- Automate data exchange between different systems, reducing manual data entry and errors.
- Gain a comprehensive view of business operations by consolidating data from multiple sources.
- Improve decision-making by providing real-time access to accurate and up-to-date information.
- Increase operational efficiency by eliminating redundant tasks and streamlining workflows.
Common ERP Integrations
Common ERP integrations include:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems: Integrate with ERP to manage customer interactions, track sales opportunities, and provide customer service.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM) systems: Integrate with ERP to manage inventory, procurement, and logistics.
- Human Capital Management (HCM) systems: Integrate with ERP to manage employee data, payroll, and benefits.
- Financial Management systems: Integrate with ERP to manage financial accounting, budgeting, and reporting.
Key Challenges and Considerations
When planning an ERP integration, it is important to consider the following challenges and factors:
- Data mapping: Ensuring that data is accurately mapped between different systems.
- Data security: Maintaining the security and integrity of data during integration.
- System compatibility: Ensuring that the systems being integrated are compatible with each other.
- Business process alignment: Aligning business processes to support the integrated systems.
- Integration costs: Considering the costs associated with integration, including software, hardware, and implementation.
Integration Methods
Integrating Oracle ERP with other systems is crucial for seamless data exchange and efficient business operations. Various integration methods are available, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
API-based Integration
API (Application Programming Interface) integration involves using pre-built interfaces to connect Oracle ERP with external systems. It allows for direct communication between applications, enabling real-time data exchange.
Pros:
- Real-time data exchange
- Reduced development effort
- Increased flexibility and scalability
Cons:
- Requires technical expertise
- May require licensing fees
Middleware-based Integration
Middleware-based integration uses a third-party software layer to facilitate communication between Oracle ERP and other systems. It acts as a bridge, translating data formats and handling data transformations.
Pros:
- Supports multiple integration protocols
- Provides data transformation and mapping capabilities
- Reduces the need for custom coding
Cons:
- Can be complex to implement
- May introduce performance bottlenecks
Data Replication
Data replication involves copying data from Oracle ERP to other systems or vice versa. It ensures that data is consistent across all connected systems, but it may not be real-time.
Pros:
- Ensures data consistency
- Supports batch processing
- Relatively easy to implement
Cons:
- May not support real-time data exchange
- Can lead to data redundancy
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Integration Method
Choosing the appropriate integration method depends on several factors, including:
- Data exchange requirements (real-time vs. batch)
- Technical capabilities and expertise
- Integration budget and resources
- Long-term scalability and flexibility
Data Integration
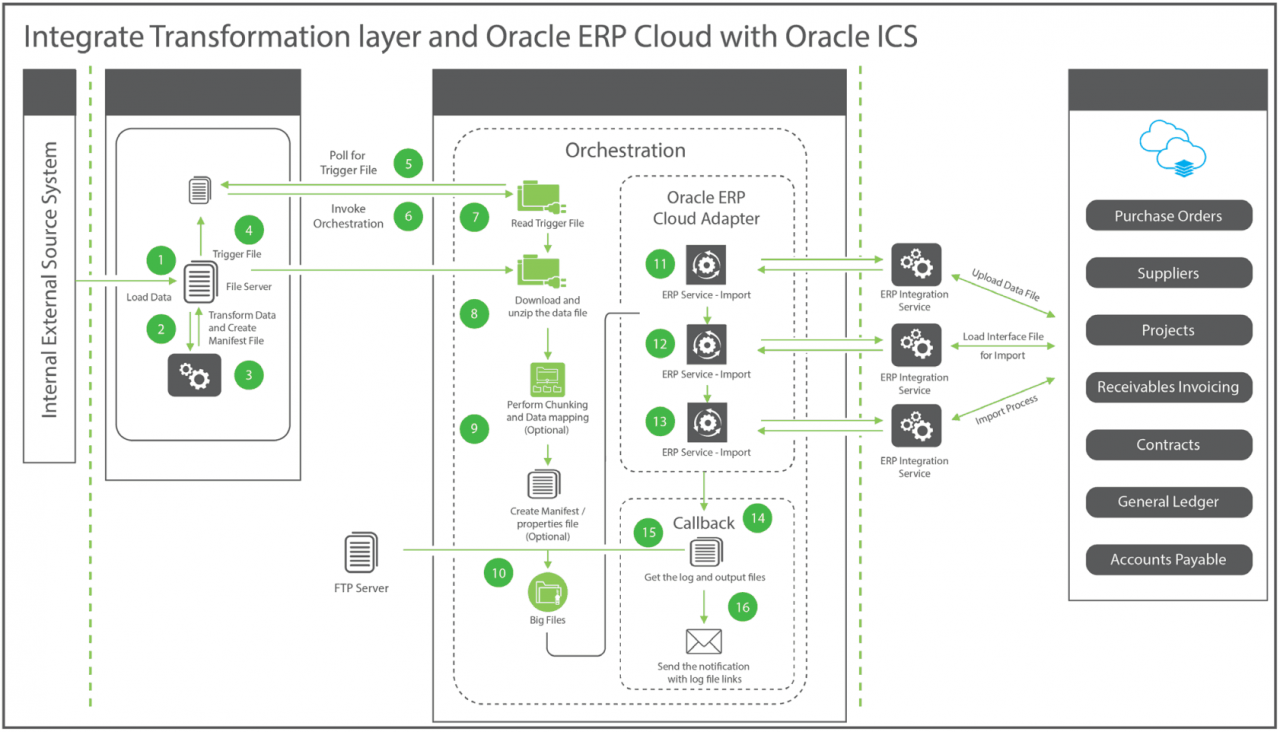
Data integration is a critical aspect of Oracle ERP implementations, as it involves connecting various data sources and ensuring seamless data flow between them. This process presents several challenges that need to be addressed to ensure successful integration.
One of the key challenges is the heterogeneity of data sources. Oracle ERP systems often need to integrate with a wide range of data sources, including legacy systems, databases, and cloud applications. Each of these data sources may have its own data structures, formats, and semantics, making it difficult to map and transform data effectively.
Another challenge is the volume and complexity of data. Oracle ERP systems typically handle large volumes of data, and the data can be complex and interconnected. This makes it difficult to ensure data accuracy and consistency during integration.
Best Practices for Data Mapping, Transformation, and Synchronization
To overcome these challenges, it is important to follow best practices for data mapping, transformation, and synchronization.
- Data mappinginvolves defining the relationships between data elements in the source and target systems. This process requires a thorough understanding of the data structures and semantics of both systems.
- Data transformationinvolves converting data from the source format to the target format. This may involve changing data types, applying business rules, or performing calculations.
- Data synchronizationensures that data is consistent across all integrated systems. This involves periodically updating data in the target systems to reflect changes made in the source systems.
By following these best practices, organizations can ensure the accuracy, consistency, and timeliness of data in their Oracle ERP systems.
Importance of Data Quality and Governance in ERP Integrations
Data quality and governance are critical to the success of Oracle ERP integrations. Poor data quality can lead to errors, inconsistencies, and inefficiencies in the ERP system. Data governance ensures that data is managed consistently and in accordance with business policies.
Organizations should implement data quality and governance processes to ensure that data is accurate, complete, consistent, and timely. This includes establishing data quality standards, implementing data validation and cleansing procedures, and monitoring data quality metrics.
By investing in data quality and governance, organizations can improve the reliability and effectiveness of their Oracle ERP systems.
Process Integration
Process integration connects different business systems and applications, allowing them to share data and functionality seamlessly. It enables organizations to automate and streamline their business processes, resulting in improved efficiency, reduced costs, and better decision-making.
There are several types of process integrations, including:
Workflow Integration
Workflow integration automates sequential or parallel tasks within a business process. It defines the steps involved in a process, assigns them to specific individuals or systems, and ensures that tasks are completed in the correct order and within specified timeframes.
Event-Driven Integration, Oracle erp integration
Event-driven integration triggers specific actions or processes based on predefined events. When an event occurs, such as a new customer order or a change in inventory levels, the integration system automatically initiates the appropriate response, such as sending an order confirmation email or updating inventory records.
Business Process Management (BPM)
BPM is a comprehensive approach to process integration that involves modeling, analyzing, and improving business processes. It provides a holistic view of all processes within an organization, enabling businesses to identify inefficiencies, eliminate bottlenecks, and optimize their operations.
Process integration can significantly improve business efficiency by:
- Eliminating manual tasks and reducing errors
- Improving communication and collaboration between different departments
- Enabling faster decision-making and response times
li>Providing real-time visibility into business processes
However, process integration also presents certain challenges, including:
- Complexity of integrating multiple systems
- Data security and privacy concerns
- Lack of standardization in process definitions
To ensure successful process integration, it is essential to follow best practices such as:
- Defining clear business objectives and requirements
- Choosing the right integration technology and vendor
- Involving all stakeholders in the integration process
- Testing and validating the integration thoroughly
- Monitoring and maintaining the integration on an ongoing basis
Security Considerations
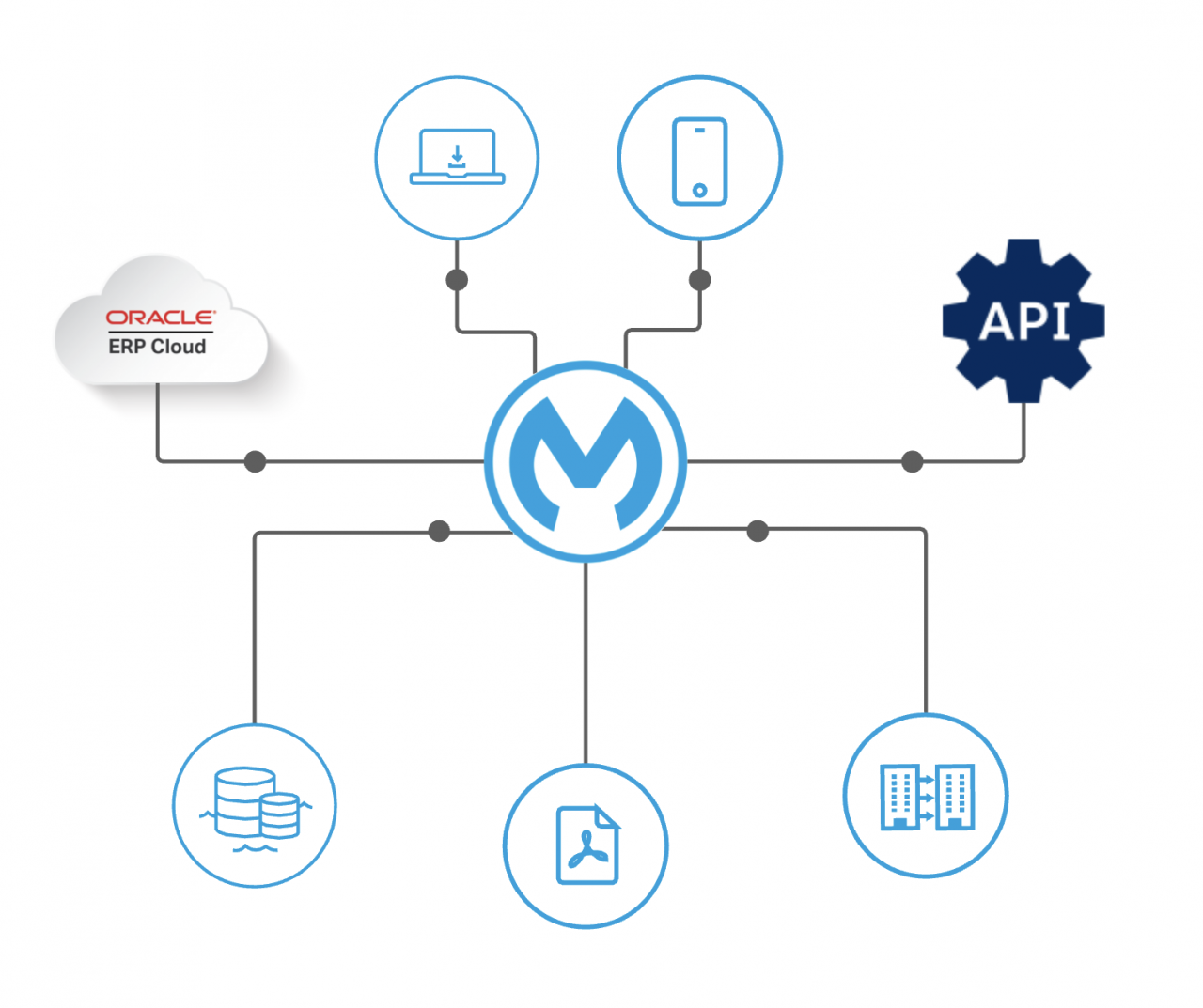
Oracle ERP integrations introduce various security risks, including unauthorized access to sensitive data, data breaches, and system vulnerabilities. To mitigate these risks, it’s crucial to implement robust security measures.
Authentication and Authorization
Establish strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication or biometrics, to prevent unauthorized access to the ERP system. Implement authorization controls to restrict access to specific data and functions based on user roles and permissions.
Data Encryption
Encrypt data at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access and interception. Use encryption protocols like SSL/TLS and strong encryption algorithms like AES-256 to ensure data confidentiality.
Vulnerability Management
Regularly scan and patch the ERP system and integrated applications for vulnerabilities. Establish a vulnerability management program to identify and address potential security risks promptly.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Ensure compliance with relevant industry standards and regulatory requirements, such as PCI DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR. These regulations mandate specific security measures to protect sensitive data and maintain compliance.
Best Practices and Case Studies
Successful Oracle ERP integration projects require a comprehensive approach that considers best practices, case studies, and emerging trends. This section provides insights into industry-proven strategies and real-world examples to guide organizations in achieving successful ERP integrations.
Best Practices
- Establish a clear project plan and governance structure.
- Involve key stakeholders throughout the integration process.
- Choose an integration approach that aligns with business objectives.
- Test and validate the integration thoroughly.
- Monitor and maintain the integration post-implementation.
Case Studies
Numerous organizations have successfully implemented Oracle ERP integrations, achieving significant benefits. Some notable case studies include:
- Company A:Improved operational efficiency by 20% through integration with Oracle E-Business Suite.
- Company B:Enhanced customer satisfaction by 15% by integrating Oracle CRM with their ERP system.
Industry Trends and Emerging Technologies
The ERP integration landscape is constantly evolving. Key trends include:
- Increased adoption of cloud-based ERP solutions.
- Emergence of low-code/no-code integration tools.
- Growing emphasis on data governance and security.
Closing Summary
As we conclude our exploration of Oracle ERP integration, it is evident that this technology has emerged as a cornerstone of modern business operations. By embracing the principles Artikeld in this discourse, organizations can unlock a new era of efficiency, collaboration, and growth.
Originally posted 2024-05-20 15:29:06.
 Bussines News Daily
Bussines News Daily