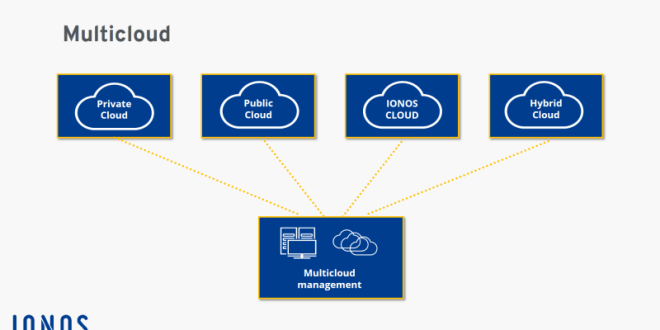
Multicloud Management Platform – The industry is adopting the multicloud strategy at a rapid pace, for example to avoid vendor lock-in or to leverage the best features of different clouds. Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure remain the top three clouds in the infrastructure services and cloud platforms category (referred to as public clouds in this article). At the same time, other public clouds such as Alibaba Cloud, IBM Cloud and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) are quickly catching up. While companies plan to have two or more public clouds, many also have an on-premise presence. With the existence of multiple cloud platforms, including hybrid cloud, there is an increased need for consistent management and governance across all cloud platforms. To take advantage of this opportunity, many providers, including cloud providers, offer multicloud management solutions. At the same time, the implementation of management and governance is very specific to the organization’s organizational structure, internal systems and controls. You must carefully determine which solutions can meet your needs. This article will help you with this identification. It examines different functional areas of multicloud management solutions and provides considerations and optimal ways to implement these functions in different contexts.
According to Gartner (see reference in the next section), there are more than 90 vendors offering multicloud management solutions (MCMS). Many of these solutions work not only on public clouds, but also with hybrid clouds. This article categorizes multicloud management solutions into the following three areas.
Multicloud Management Platform
Complete multicloud management solutions from providers that do not provide their own cloud. These solutions are commonly referred to as Cloud Management Platforms (CMPs) because they support a variety of features to manage multiple clouds. For example Flexera CMP, Scalr CMP, Morpheus CMP. The main features of these solutions are:
Functional Architecture For Multi Cloud Management Platform
Solutions from cloud providers themselves. For example, Azure Arc, Azure Cost Management, Google Anthos, IBM Multi Cloud Management. The main features of these solutions are:
These solutions only cover a certain functional area and run in clouds. The main features of these solutions are:
As multicloud becomes more popular, vendors are adding more features for multicloud management. These characteristics can be divided into higher-level characteristic areas. This article groups these functionalities into eight functional areas, which Gartner defines as required functional areas of a CMP in its 2020 Magic Quadrant for CMP. If you don’t have a Garner subscription, you can download a free copy of Flexera. These functional areas are:
Gartner listed seven CMP vendors in its 2020 Magic Quadrant: CloudBolt, Flexera, HyperGrid, Morpheus Data, Scalr, Snow Software-Embotics, VMware. Every provider has its strengths and limitations. When organizations adopt a CMP, they may not utilize all of the functional areas provided by the CMP. They may be leveraging features that are more relevant to their cloud environment. At the same time, they may also use other types of solutions (solutions from cloud providers or function-specific specialized solutions). The diagram above shows the landscape of multicloud management solutions with different functional areas and solution types.
Business Drivers And Challenges When Adopting A Multicloud Strategy
Many organizations have been using the public cloud for many years and already have very mature cloud governance and management processes. They may already be using some solutions that have multicloud capabilities. As multicloud adoption increases within an organization, you may need additional multicloud management capabilities. At the same time, you need to ensure that this solution fits your management and governance processes. The following sections describe each functional area and provide key considerations for identifying the solution/tool for that area.
Some examples of features in this area include: End User Deployment Portal, Deployment Templates, Deployment Automation, and Workflows. The key challenges/considerations in this area are:
Tools like Ansible and Terraform are already very popular in the industry. Your company may already be using one of these to automate infrastructure provisioning. If you use Ansible Playbooks or Terraform, you can use native Ansible modules or Terraform cloud provider modules. If the tool-specific module is not available, you have the option to access cloud-native modules such as Azure Resource Management (ARM) or Google Cloud templates. Deployment Manager templates. These approaches give you a lot of flexibility in adding specific security/governance controls for your organization. Additionally, you can always write a new playbook/configuration file if you need to automate the newly released feature or service. You should consider whether the cloud management solution can provide you with the same flexibility you need to implement specific controls for your business.
Some examples of features in this area include service catalog, catalog spending limits, and application approval workflows. The considerations in this area are:
Multi Cloud Management Platforms Flowchart
Some examples of features in this area are resource discovery and inventory, configuration policies and change tracking, cloud platform native tag integration, untagged resource discovery and actions. Accurately discovering and inventorying all of your cloud resources is an essential part of governance. Most cloud providers provide APIs and tools to retrieve your inventory. MCMS leverages these APIs/tools to provide a single, centralized dashboard. This central dashboard of your resources, organized by object or department, is the main advantage of this functional area. The considerations in this area are:
Some examples of features in this area are centralized log collection, dashboards, alerts, etc. This is another important and challenging area for multi-cloud management. All cloud providers have native logging and monitoring tools with advanced features such as Azure Monitor (formerly Application Insights and Log Analytics), Google Cloud Monitoring (formerly Stack Driver), and AWS CloudWatch. To have centralized logging or monitoring dashboards, you may need to export/stream data from each cloud to your central tool. The considerations in this area are:
Some examples of features in this area include cost tracking reports and dashboards, budget definition and alert policies, and custom pricing for internal cross-loading. This was one of the first features of multicloud management solutions. Public clouds are making it increasingly easier to provide resources with virtually unlimited capacity. As a result, without adequate governance, companies find that the cost of cloud usage increases very quickly. This functional area is critical for centralized cost control through multiple levels of budget definition and detailed reporting. The considerations in this area are:
In general, migration, backup and disaster recovery (DR) are three areas with different characteristics. Backup methods are often used to migrate from on-premises to the cloud. Additionally, data recovery from backups is used for disaster recovery. These factors appear to be why Gartner has combined these three areas into one in the CMP Magic Quadrant. However, Gartner primarily lists backup-related features in this area. For example, backup for different storage types: object storage, block storage, computing. This is a relatively new area for CMPs, so the capabilities of this area are still mature. The considerations in this area are:
Multi Cloud Management: Definition, Challenges, And Benefits
Some examples of features in this area include role-based access control (RBAC), cloud platform native console SSO, IAM and network policies, security event notifications, security configuration management, and compliance assessment. This is a very broad area; A single platform or tool may not cover all functions in their entirety. In addition, some features may be covered by, overlap with, or depend on features in other areas covered above. For example, security event notification can be covered by a log monitoring and analysis tool such as Sumo Logic; The compliance score may depend on the tagging functionality provided by the Inventory and Classification functional area. The considerations in this area are:
This feature area is more about the packaging and deployment capabilities of CMPs than their multi-cloud management capabilities. Some examples include integration with cloud providers, API exposure over SSL, authentications over SAML-based SSO, self-service support resources, support plans, and 24/7 incident support, 7 days from today The considerations in this area are general considerations you make when evaluating a vendor’s product.
Multicloud management solutions have developed significantly in the recent past and offer extensive functions. CMPs provide a comprehensive package of multiple functional areas that support most public clouds. At the same time, cloud providers have begun to offer solutions in some functional areas that allow you to manage these functions in hybrid and multicloud environments. Additionally, there are specialized solutions that offer industry-leading capabilities in your area of expertise. For your business, a single provider or CMP solution may or may not meet all your needs. For large organizations that are already mature in their cloud adoption, you may need specific solutions for individual functional areas. Some of these areas may leverage vendor solutions or cloud-native offerings, while other solutions may require custom development. You should evaluate your multicloud management needs in each capacity and then select the right solution or solutions for your business. 84% of companies have a multi-cloud strategy and 58% use both public and private clouds as part of this strategy.
While the benefits are significant, we cannot ignore the challenges that come with adopting a multi-cloud strategy: multiple competencies and vendors to manage complex migration processes.
What Is Multicloud Infrastructure? Definition, Components, And Management Best Practices
Since not all tools are created equal, in this article I will shed some light on the best multi-cloud management platform on the market and explain what makes it so great.
Designed specifically for enterprise scale, Scalr helps standardize usage, control costs, and allows users to choose the best cloud services for their needs without being locked into a provider. It offers unmatched flexibility and efficiency and the best part is that it allows you to be creative
Multicloud management solution, hybrid multicloud platform, cloud pak for multicloud management, multicloud cost management, ibm multicloud management, multicloud log management, multicloud management platform gartner, multicloud management platform ibm, multicloud management software, ibm cloud pak for multicloud management, multicloud management, multicloud management tools
 Bussines News Daily
Bussines News Daily