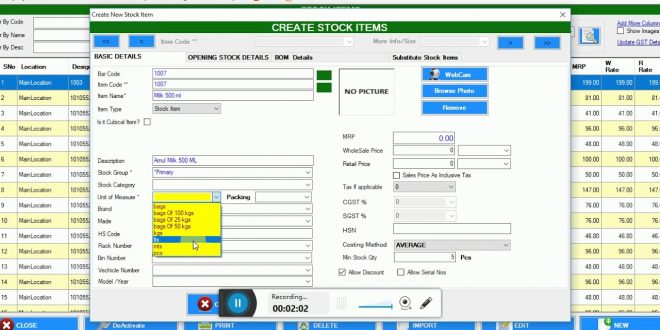
Low cost ERP systems have emerged as a game-changer for businesses seeking cost-effective and efficient solutions to streamline their operations. These systems offer a wide range of benefits, from cost savings to increased accessibility, making them an ideal choice for small businesses and startups.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the concept of low cost ERP, its key features and functionalities, and the factors to consider when selecting a system. We will also explore best practices for implementation, integration, and ongoing management to ensure a successful ERP deployment.
Low Cost ERP Overview

Low cost ERP systems are designed to provide businesses with an affordable way to manage their operations. These systems typically offer a core set of features, such as financial management, inventory management, and customer relationship management (CRM). Low cost ERP systems are often cloud-based, which makes them easy to implement and maintain.
There are many benefits to using a low cost ERP system. These benefits include:
- Affordability:Low cost ERP systems are typically much more affordable than traditional ERP systems.
- Ease of implementation:Low cost ERP systems are often cloud-based, which makes them easy to implement and maintain.
- Scalability:Low cost ERP systems can be scaled up or down to meet the needs of a growing business.
- Flexibility:Low cost ERP systems are often highly customizable, which allows businesses to tailor the system to their specific needs.
There are a number of key features and functionalities that are typically found in low cost ERP systems. These features include:
- Financial management:Low cost ERP systems typically include features for managing accounts payable, accounts receivable, and general ledger.
- Inventory management:Low cost ERP systems typically include features for managing inventory levels, tracking inventory movements, and generating purchase orders.
- Customer relationship management (CRM):Low cost ERP systems typically include features for managing customer contact information, tracking sales opportunities, and generating marketing campaigns.
There are a number of vendors that offer low cost ERP systems. Some of the most popular vendors include:
- NetSuite:NetSuite is a cloud-based ERP system that is designed for small and medium-sized businesses.
- SAP Business One:SAP Business One is a cloud-based ERP system that is designed for small and medium-sized businesses.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central:Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central is a cloud-based ERP system that is designed for small and medium-sized businesses.
Benefits of Low Cost ERP
Low-cost ERP offers significant advantages to businesses, particularly small businesses and startups. These benefits include:
Cost savings: Low-cost ERP systems are typically priced on a subscription basis, making them more affordable than traditional on-premise ERP solutions. This can free up capital for other business needs.
Efficiency improvements: Low-cost ERP systems can help businesses streamline their operations and improve efficiency. By automating tasks and providing real-time visibility into data, these systems can help businesses reduce costs and improve productivity.
Increased Accessibility and Flexibility
Low-cost ERP systems are often cloud-based, which means that they can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection. This makes them ideal for businesses with remote employees or multiple locations. Cloud-based ERP systems are also more flexible than on-premise systems, allowing businesses to scale up or down as needed.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Many businesses have successfully implemented low-cost ERP systems. Here are a few examples:
- A small manufacturing company implemented a low-cost ERP system and saw a 20% reduction in costs and a 15% increase in productivity.
- A retail chain implemented a low-cost ERP system and saw a 10% increase in sales and a 5% decrease in operating costs.
These are just a few examples of the benefits that low-cost ERP systems can offer businesses. If you are looking for a way to improve your business’s efficiency and profitability, a low-cost ERP system may be the right solution for you.
Considerations for Choosing Low Cost ERP
Selecting a low-cost ERP system requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure it aligns with your business needs and long-term goals. Scalability, customization, and integration capabilities are crucial aspects that should be thoroughly evaluated.
Scalability
Consider the potential growth of your business and choose an ERP system that can scale accordingly. The system should be able to handle increasing data volumes, transactions, and users without compromising performance or requiring significant additional investment.
Customization
No two businesses are exactly alike. Look for an ERP system that offers customization options to tailor the solution to your specific requirements. This flexibility allows you to adapt the system to your unique processes, workflows, and industry-specific needs.
Integration Capabilities
ERP systems should seamlessly integrate with other business applications, such as CRM, accounting, and supply chain management systems. This integration ensures data consistency, eliminates manual data entry, and streamlines business processes.
Tips for Evaluating and Comparing Vendors
- Define your business requirements clearly before starting your search.
- Research and shortlist potential vendors based on their industry experience and product offerings.
- Request demos and trial versions to evaluate the functionality and user-friendliness of the systems.
- Consider the vendor’s reputation, support offerings, and implementation track record.
- Negotiate pricing and licensing terms that align with your budget and business needs.
Implementation and Deployment
Implementing a low cost ERP system involves several key steps:
1. Planning and Preparation:Define project scope, identify stakeholders, and establish a project plan.
2. Data Migration:Transfer existing data from legacy systems to the new ERP system.
3. System Configuration:Customize the ERP system to meet specific business requirements.
4. User Training:Provide training to end-users on the new ERP system.
5. Go-Live:Launch the ERP system and begin using it for daily operations.
Challenges and Best Practices
Deploying a low cost ERP system presents several challenges:
- Data Integration:Ensuring seamless data flow between the ERP system and other business applications.
- User Adoption:Encouraging users to embrace the new system and its functionalities.
- Process Changes:Adapting business processes to align with the ERP system’s capabilities.
To overcome these challenges, it is recommended to:
- Involve stakeholders throughout the implementation process.
- Communicate effectively to keep users informed and engaged.
- Provide comprehensive training and support to users.
Timeline and Resource Allocation, Low cost erp
The timeline for ERP implementation can vary depending on the size and complexity of the organization. However, a typical implementation can take several months to complete.Resource allocation should consider the following:
- Project Manager:Oversees the overall implementation process.
- Technical Team:Responsible for system configuration and data migration.
- Business Analysts:Assist with process mapping and requirements gathering.
- End-Users:Participate in training and testing.
Integration with Other Systems
Integrating low-cost ERP with other business systems is crucial for streamlining operations, enhancing data visibility, and improving decision-making. By connecting ERP with key applications, businesses can automate processes, eliminate data silos, and gain a comprehensive view of their operations.
Methods and tools for ERP integration include:
- Application programming interfaces (APIs): APIs allow different systems to communicate and exchange data.
- Enterprise service bus (ESB): An ESB acts as a central hub for data exchange between various applications.
- Data integration tools: These tools provide pre-built connectors and mapping capabilities to simplify data integration.
CRM Integration
Integrating ERP with customer relationship management (CRM) systems enables businesses to manage customer interactions, track sales pipelines, and provide personalized customer experiences. This integration allows for seamless data flow between sales, marketing, and customer service teams, improving collaboration and efficiency.
Accounting Integration
ERP integration with accounting systems ensures accurate and timely financial reporting. By automating the flow of financial data between the two systems, businesses can streamline accounting processes, reduce errors, and improve compliance.
Benefits of ERP Integration
- Improved data accuracy and consistency
- Increased operational efficiency
- Enhanced decision-making
- Reduced costs and improved ROI
- Better customer service
Examples of Successful ERP Integrations
- A manufacturing company integrated its ERP with a CRM system to improve customer relationship management and increase sales.
- A retail chain integrated its ERP with an accounting system to automate financial reporting and reduce errors.
Best Practices for Low Cost ERP Management
Implementing and managing a low-cost ERP system effectively requires careful planning and ongoing attention. Here are some best practices to help you get the most out of your investment:
Effective management of a low-cost ERP system is essential to ensure its continued success and value to the organization. By following these best practices, you can optimize the performance of your ERP system, minimize risks, and maximize its benefits.
Data Governance
- Establish clear data ownership and responsibilities.
- Implement data validation and integrity rules.
- Regularly review and cleanse data to ensure accuracy and consistency.
Security
- Implement strong user authentication and authorization mechanisms.
- Regularly update security patches and software.
- Monitor system activity and implement intrusion detection and prevention measures.
User Training
- Provide comprehensive training to users on all aspects of the ERP system.
- Offer ongoing support and resources to users.
- Encourage user feedback and involvement in system improvements.
Ongoing Maintenance and Optimization
- Regularly review and update the ERP system to ensure it meets changing business needs.
- Monitor system performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Implement regular backups and disaster recovery procedures.
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, low cost ERP systems provide businesses with a powerful tool to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and gain a competitive edge. By carefully evaluating their needs, choosing the right vendor, and implementing best practices, businesses can leverage the full potential of low cost ERP to drive growth and success.
Originally posted 2024-05-20 14:33:00.
 Bussines News Daily
Bussines News Daily