Delving into the realm of logistics ERP software, this comprehensive guide embarks on a journey to unravel the intricacies of this transformative technology. From its fundamental principles to its far-reaching implications, we delve into the depths of logistics ERP software, exploring its key components, integration capabilities, implementation best practices, and emerging trends that are shaping the future of supply chain management.
Logistics ERP software stands as a cornerstone of modern supply chain management, offering a unified platform that seamlessly integrates and automates critical logistics processes. Its comprehensive suite of features empowers businesses to optimize inventory management, streamline warehouse operations, enhance transportation efficiency, and expedite order fulfillment, leading to significant improvements in operational efficiency, cost reduction, and customer satisfaction.
Definition and Overview of Logistics ERP Software
Logistics ERP software is a comprehensive business management solution that integrates all aspects of logistics operations, including inventory management, order fulfillment, transportation management, and customer relationship management (CRM).
By centralizing all logistics data and processes in a single system, logistics ERP software can help businesses improve efficiency, reduce costs, and gain a competitive advantage.
Key Features and Functionalities
- Inventory management
- Order fulfillment
- Transportation management
- Customer relationship management (CRM)
- Reporting and analytics
Benefits of Implementing Logistics ERP Software
- Improved efficiency
- Reduced costs
- Increased customer satisfaction
- Improved decision-making
- Enhanced visibility and control
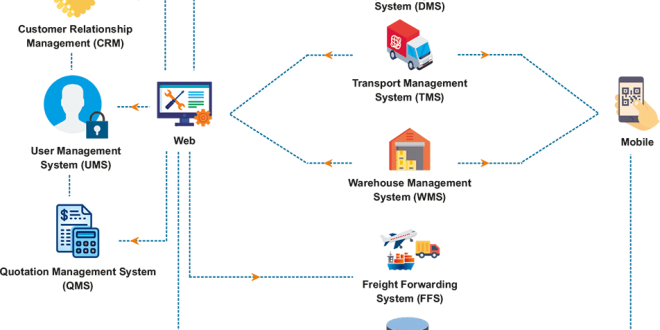
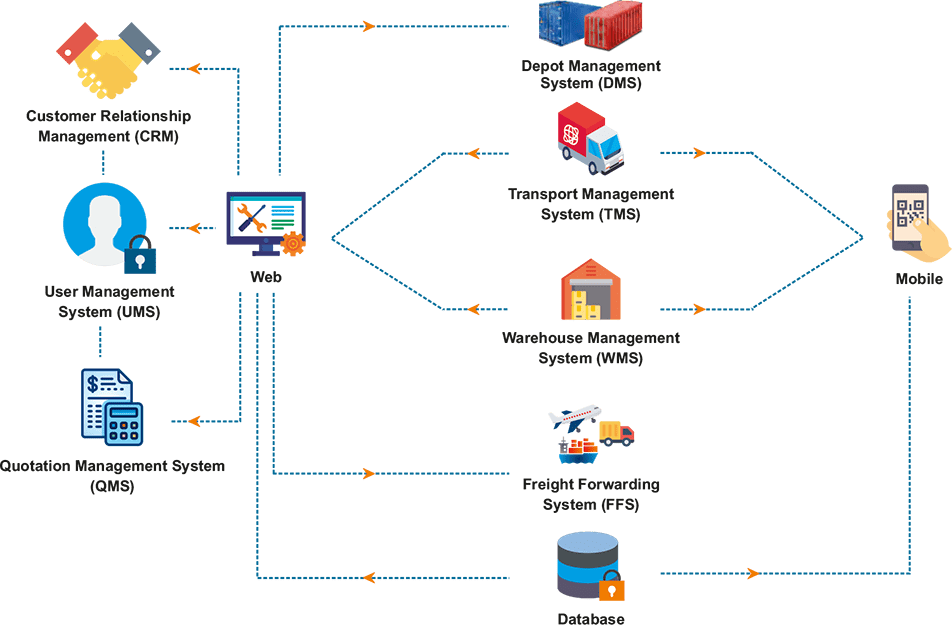
Key Components of Logistics ERP Software
Logistics ERP software encompasses a comprehensive suite of modules that cater to various aspects of supply chain management. These components work in synergy to provide a holistic view of the logistics operations, enabling businesses to optimize their processes, enhance efficiency, and gain a competitive edge.
The core components of logistics ERP software include:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Inventory Management | Centralizes inventory data across multiple locations, providing real-time visibility into stock levels, availability, and movement. Facilitates inventory planning, forecasting, and replenishment to ensure optimal stock levels and minimize inventory carrying costs. |
| Warehouse Management | Manages warehouse operations, including receiving, put-away, storage, picking, packing, and shipping. Optimizes warehouse space utilization, improves picking and packing efficiency, and reduces order fulfillment lead times. |
| Transportation Management | Plans, executes, and monitors the movement of goods from suppliers to warehouses and from warehouses to customers. Provides visibility into carrier performance, optimizes shipping routes, and reduces transportation costs. |
| Order Fulfillment | Automates the process of receiving, processing, and fulfilling customer orders. Integrates with inventory management and warehouse management modules to ensure accurate order picking, packing, and shipping, enhancing customer satisfaction and reducing order fulfillment errors. |
Integration with Other Business Systems

Seamless integration between logistics ERP software and other business systems is crucial for optimizing operations and achieving end-to-end visibility.
Integrating logistics ERP with finance systems streamlines financial transactions, eliminates manual data entry, and provides real-time financial data for informed decision-making. Integration with sales systems enables real-time order fulfillment tracking, inventory updates, and automated invoicing. By integrating with customer service systems, logistics ERP can provide up-to-date shipment status, delivery information, and proactive customer support.
Benefits of Integration
- Improved data accuracy and consistency across departments.
- Reduced operational costs by eliminating manual processes.
- Enhanced customer satisfaction through real-time visibility and proactive support.
- Increased efficiency and productivity by automating tasks and streamlining workflows.
Examples of Successful Integrations
- A global manufacturing company integrated its logistics ERP with its finance system, resulting in a 20% reduction in order processing time and a 15% increase in inventory accuracy.
- A leading retailer integrated its logistics ERP with its sales system, enabling real-time inventory updates and automated order fulfillment, leading to a 30% increase in sales and a 25% reduction in customer complaints.
4. Implementation and Best Practices
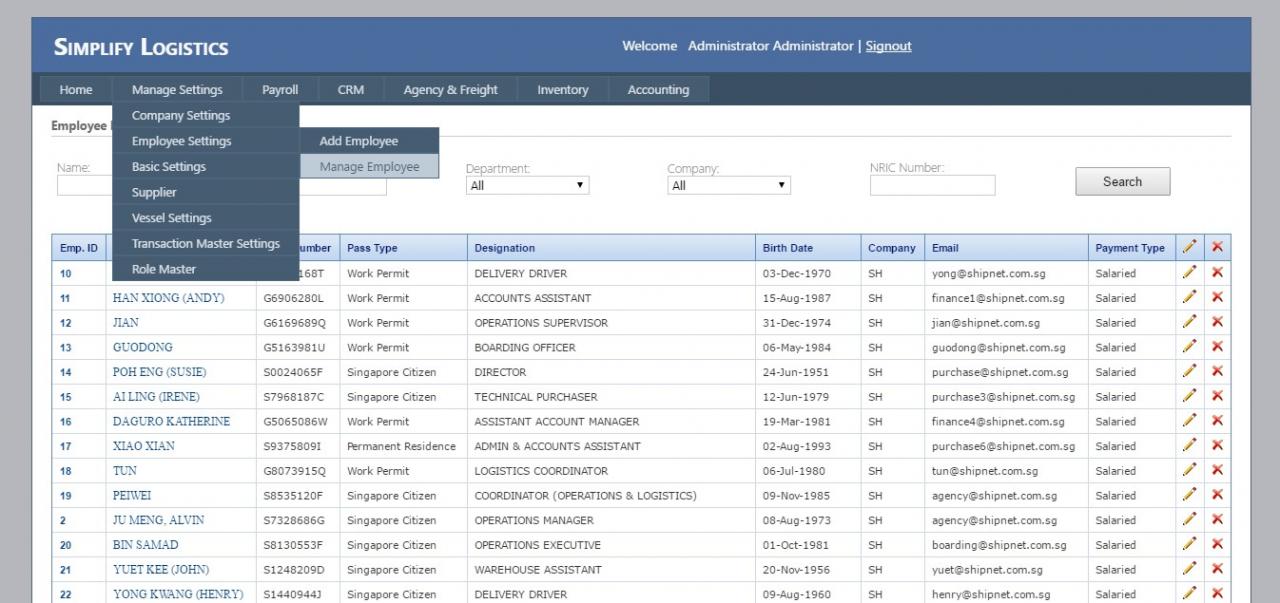
Implementing logistics ERP software involves a structured process to ensure a successful deployment. Key steps include planning, data migration, and user training.
- Planning:Defining project scope, timelines, and resource allocation. Establishing a project team with expertise in logistics, IT, and business processes.
- Data Migration:Extracting and cleansing data from legacy systems to ensure data integrity and accuracy. Developing a comprehensive data migration plan to minimize disruptions.
- User Training:Providing comprehensive training to end-users on the new software’s functionality and processes. Ensuring users are equipped to leverage the system effectively.
Best practices for implementation include:
- Stakeholder Involvement:Engaging key stakeholders throughout the process to gather requirements and ensure alignment.
- Phased Approach:Implementing the software in phases to minimize disruption and allow for incremental adoption.
- Data Validation:Verifying data accuracy and completeness before and after migration to maintain data integrity.
- Continuous Monitoring:Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) and user feedback to identify areas for improvement and ensure ongoing success.
Case studies of successful implementations demonstrate the benefits of logistics ERP software, including improved efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced customer service. Lessons learned from these case studies provide valuable insights for organizations considering implementation.
5. Challenges and Considerations
Implementing and using logistics ERP software can bring about a host of benefits, but it is not without its challenges. Understanding these potential hurdles and devising strategies to mitigate them can help ensure a smooth transition and maximize the value of the software.
Data Integration and Quality, Logistics erp software
- Integrating data from multiple sources can be complex and time-consuming.
- Ensuring data accuracy and consistency is crucial for effective decision-making.
- Data quality issues can lead to errors, inefficiencies, and poor decision-making.
Process Changes and User Adoption
- Implementing new software often requires changes to existing processes.
- Resistance to change can be a significant barrier to successful implementation.
- User training and support are essential for ensuring effective adoption and utilization of the software.
Cost and Complexity
- Logistics ERP software can be expensive to purchase, implement, and maintain.
- The complexity of the software can require specialized expertise for implementation and support.
- Hidden costs, such as training, data migration, and ongoing maintenance, should be considered.
Technical Issues and Downtime
- Technical glitches and downtime can disrupt operations and cause significant losses.
- Proper hardware, software, and network infrastructure are essential for reliable performance.
- Regular maintenance and updates are crucial to minimize the risk of downtime.
Pitfalls and Recommendations
- Underestimating the complexity of data integration and quality.
- Ignoring the need for process changes and user training.
- Not considering the total cost of ownership, including hidden costs.
- Failing to ensure reliable hardware, software, and network infrastructure.
To avoid these pitfalls, organizations should:
- Thoroughly assess data sources and quality before integration.
- Plan for comprehensive process changes and user training.
- Evaluate the total cost of ownership and secure necessary funding.
- Invest in reliable hardware, software, and network infrastructure.
Trends and Future of Logistics ERP Software
The logistics industry is undergoing a period of rapid transformation, driven by the rise of e-commerce, globalization, and the increasing complexity of supply chains. Logistics ERP software is playing a vital role in this transformation, helping businesses to streamline their operations, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive advantage.
In the future, we can expect to see even greater innovation in logistics ERP software, with the emergence of new technologies such as cloud-based solutions, artificial intelligence, and machine learning. These technologies will help businesses to further automate their operations, gain real-time visibility into their supply chains, and make better decisions.
Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud-based logistics ERP software is becoming increasingly popular, as it offers businesses a number of advantages, including:
- Reduced IT costs
- Increased flexibility and scalability
- Improved collaboration and data sharing
- Enhanced security
As more and more businesses move to the cloud, we can expect to see cloud-based logistics ERP software become the standard.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is another emerging technology that is having a major impact on the logistics industry. AI can be used to automate a wide range of tasks, including:
- Predictive analytics
- Demand forecasting
- Inventory management
- Route optimization
By leveraging AI, businesses can improve the efficiency of their operations, reduce costs, and gain a competitive advantage.
Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a subset of AI that allows computers to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. ML can be used to improve the accuracy of predictive analytics, demand forecasting, and other logistics-related tasks.
As ML technology continues to develop, we can expect to see even greater innovation in logistics ERP software. ML will help businesses to automate more tasks, gain real-time visibility into their supply chains, and make better decisions.
How Businesses Can Stay Ahead of the Curve
To stay ahead of the curve in the rapidly changing logistics industry, businesses need to invest in logistics ERP software that is:
- Cloud-based
- AI-enabled
- ML-powered
By investing in these technologies, businesses can improve the efficiency of their operations, reduce costs, and gain a competitive advantage.
End of Discussion: Logistics Erp Software
In the ever-evolving landscape of supply chain management, logistics ERP software has emerged as an indispensable tool for businesses seeking to gain a competitive edge. Its ability to streamline operations, enhance visibility, and empower data-driven decision-making has transformed the way businesses manage their supply chains.
As technology continues to advance, the future of logistics ERP software holds even greater promise, with emerging trends such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and machine learning poised to revolutionize the industry once again.
Originally posted 2024-05-20 07:20:53.
 Bussines News Daily
Bussines News Daily