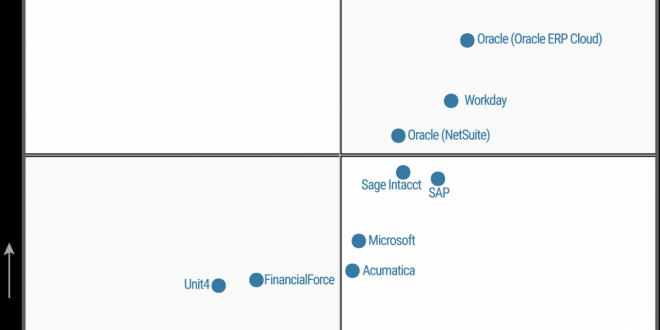
The Gartner Magic Quadrant for Cloud ERP is a comprehensive evaluation of leading vendors in the cloud ERP market. This report provides insights into the strengths, weaknesses, and key differentiators of each vendor, enabling organizations to make informed decisions about their Cloud ERP implementations.
The market overview section provides a comprehensive overview of the Cloud ERP market, discussing key trends, growth drivers, and major players. The vendor analysis section compares the strengths and weaknesses of the vendors in the Leaders quadrant, highlighting their key differentiators and value propositions.
Market Overview
The Cloud ERP market is experiencing substantial growth due to its numerous advantages over traditional on-premise ERP systems. Cloud ERP offers flexibility, scalability, and reduced IT costs, making it an attractive option for businesses of all sizes. The market is dominated by a few major players, including SAP, Oracle, and Microsoft, who hold a significant market share.
Key trends shaping the Cloud ERP market include the increasing adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies, the rise of industry-specific cloud ERP solutions, and the growing demand for cloud ERP solutions that can support global operations.
These trends are expected to continue to drive market growth in the coming years.
Major Players and Market Share
The major players in the Cloud ERP market include SAP, Oracle, Microsoft, Infor, and Workday. SAP is the market leader with a market share of over 20%. Oracle and Microsoft are also major players with market shares of over 10% each.
Infor and Workday are smaller players but have been gaining market share in recent years.
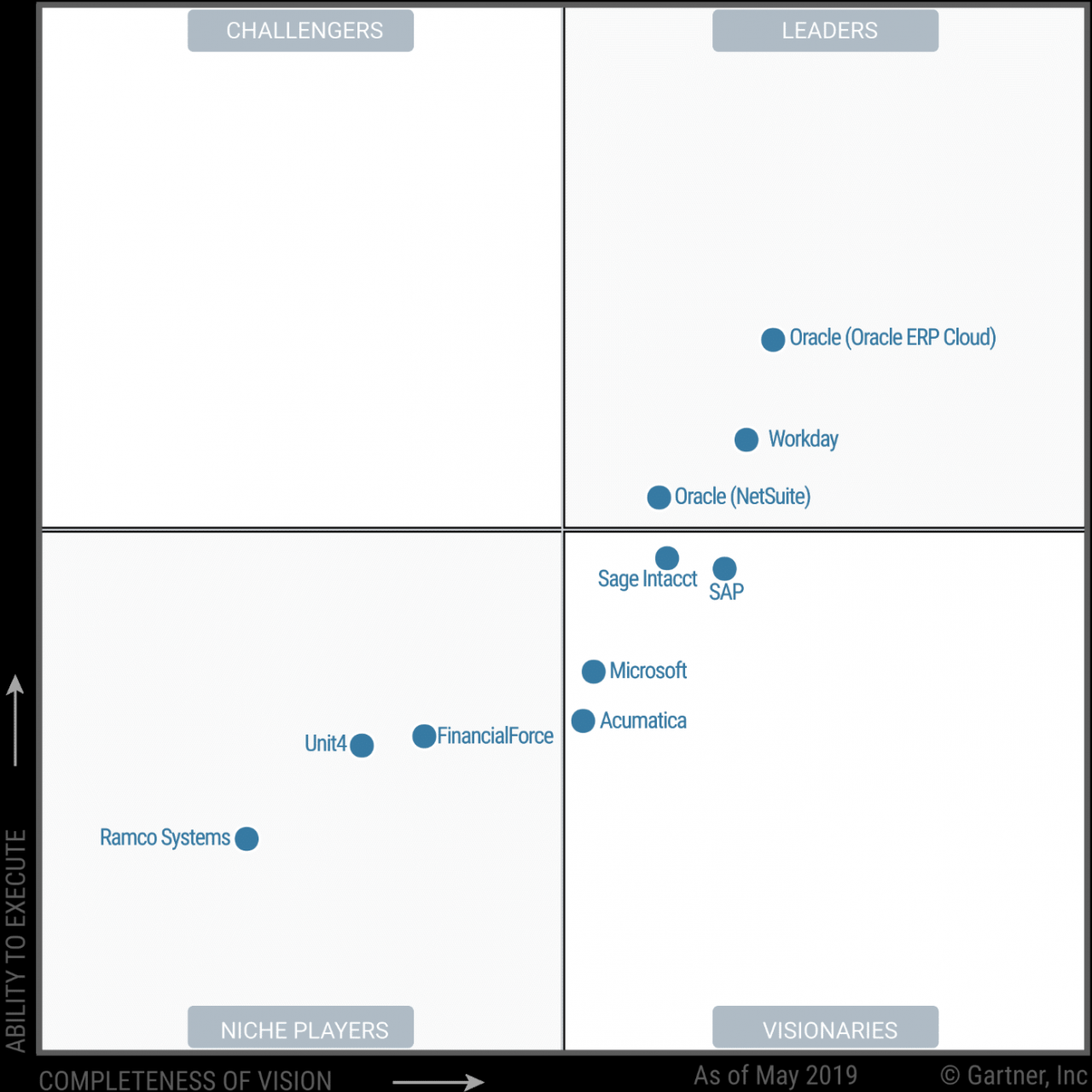
Gartner Magic Quadrant for Cloud ERP
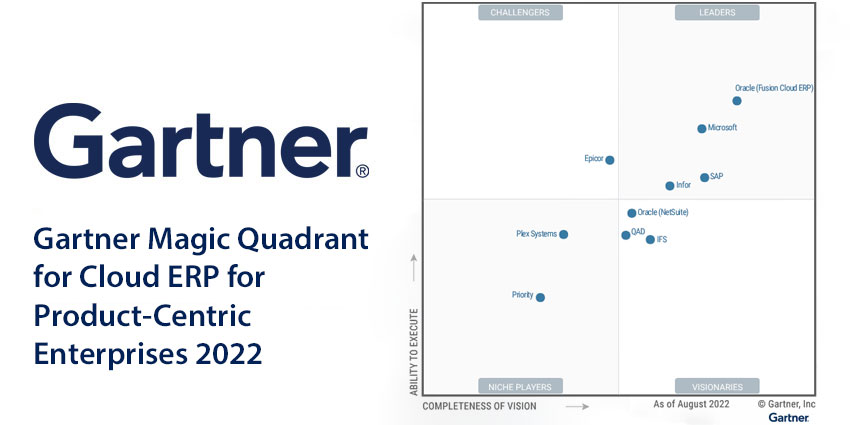
Gartner’s Magic Quadrant for Cloud ERP is a comprehensive evaluation of leading vendors in the cloud ERP market. The methodology used by Gartner involves a rigorous analysis of vendors based on their completeness of vision and ability to execute.
The Magic Quadrant is divided into four quadrants: Leaders, Challengers, Visionaries, and Niche Players. Vendors are positioned in the quadrants based on their overall performance and market presence.
Key Criteria
Gartner uses a set of key criteria to evaluate vendors in the Magic Quadrant for Cloud ERP. These criteria include:
- Functionality:The breadth and depth of the vendor’s ERP solution.
- Usability:The ease of use and user experience of the vendor’s solution.
- Scalability:The ability of the vendor’s solution to scale to meet the needs of growing businesses.
- Reliability:The uptime and performance of the vendor’s solution.
- Security:The level of security provided by the vendor’s solution.
Vendors Positioned in the Magic Quadrant
The following vendors are positioned in the Magic Quadrant for Cloud ERP:
Leaders
- SAP
- Oracle
- Microsoft
Challengers
- Infor
- Epicor
- NetSuite
Visionaries
- Workday
- Sage Intacct
- Acumatica
Niche Players
- Ramco Systems
- Unit4
- Odoo
Vendor Analysis: Gartner Magic Quadrant For Cloud Erp
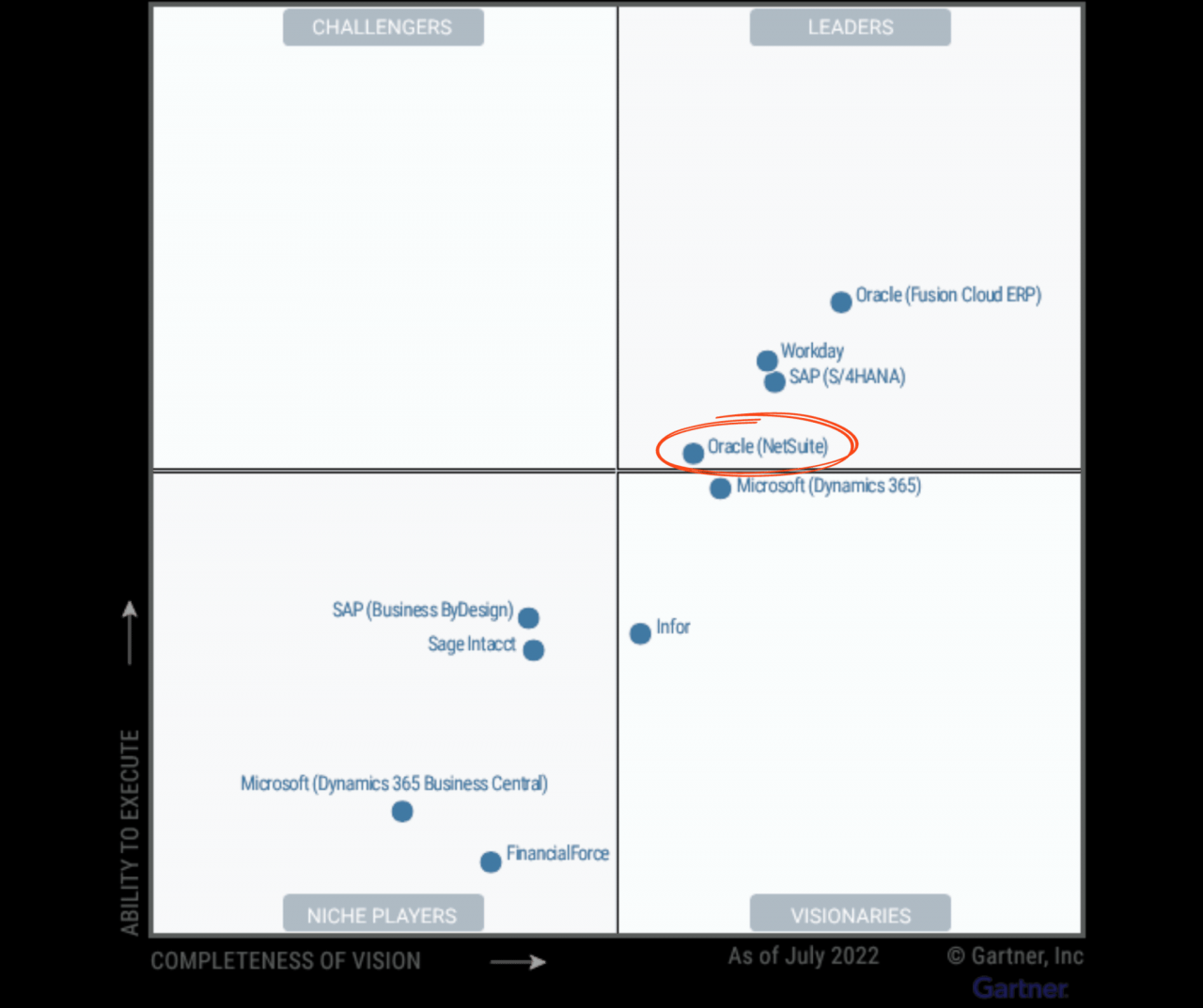
The Leaders quadrant in the Gartner Magic Quadrant for Cloud ERP comprises vendors that demonstrate a comprehensive vision and strong execution capabilities. These vendors offer robust cloud ERP solutions that meet the evolving needs of enterprises. In this section, we will compare the strengths and weaknesses of the vendors in the Leaders quadrant, discuss their key differentiators and value propositions, and provide examples of successful Cloud ERP implementations.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Vendors in the Leaders Quadrant
The following table provides a comparative analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of the vendors in the Leaders quadrant:
| Vendor | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| SAP |
|
|
| Oracle |
|
|
| Microsoft |
|
|
| Workday |
|
|
Key Differentiators and Value Propositions of Each Vendor, Gartner magic quadrant for cloud erp
Each vendor in the Leaders quadrant offers unique differentiators and value propositions that cater to specific customer needs. Here is a brief overview:
- SAP:SAP is known for its comprehensive ERP suite, strong brand recognition, and global presence. It is a suitable choice for large enterprises with complex business requirements and a need for a robust and integrated ERP solution.
- Oracle:Oracle offers a cloud-first approach with a focus on innovation and strong financial management capabilities. It is a good fit for organizations looking for a cloud-based ERP solution with advanced financial and supply chain management functionality.
- Microsoft:Microsoft’s Cloud ERP solution stands out for its ease of use, intuitive user interface, and strong integration with Microsoft products. It is ideal for organizations seeking an affordable and user-friendly ERP solution that can be easily integrated with their existing Microsoft ecosystem.
- Workday:Workday’s Cloud ERP solution is known for its human capital management (HCM) capabilities, modern interface, and cloud-native architecture. It is a suitable choice for organizations looking for a cloud-based ERP solution that prioritizes HCM and user experience.
Examples of Successful Cloud ERP Implementations by Each Vendor
- SAP:Coca-Cola, Unilever, and Volkswagen
- Oracle:AT&T, FedEx, and Walmart
- Microsoft:Starbucks, Toyota, and L’Oréal
- Workday:Amazon, Google, and Netflix
Key Considerations for Cloud ERP Selection
Selecting a Cloud ERP solution requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure alignment with organizational needs and objectives. Understanding the benefits and challenges of Cloud ERP adoption is crucial for making informed decisions.
Organizations considering Cloud ERP implementation should consider the following key aspects:
Functional Requirements
- Identify the core business processes and functional areas that require ERP support.
- Evaluate the solution’s ability to meet specific industry requirements and regulatory compliance.
- Assess the vendor’s expertise and experience in the relevant industry or business vertical.
Integration and Interoperability
- Determine the need for integration with existing on-premise systems or third-party applications.
- Evaluate the vendor’s capabilities for seamless data exchange and integration with other systems.
- Consider the solution’s ability to support open standards and industry-leading protocols.
Scalability and Flexibility
- Assess the solution’s ability to accommodate future growth and changing business needs.
- Evaluate the vendor’s support for customization, configuration, and extensibility.
- Consider the solution’s ability to handle seasonal fluctuations or unexpected demand spikes.
Security and Compliance
- Evaluate the vendor’s security measures and compliance with industry standards.
- Assess the solution’s ability to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access or breaches.
- Consider the vendor’s track record and reputation for security and compliance.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
- Calculate the upfront and ongoing costs associated with the Cloud ERP solution.
- Evaluate the vendor’s pricing model and subscription options.
- Consider the potential return on investment (ROI) and long-term cost savings.
Future Trends in Cloud ERP
The Cloud ERP market is constantly evolving, with new trends and innovations emerging all the time. These trends are shaping the future of Cloud ERP and will have a significant impact on how businesses use these solutions in the years to come.
One of the most important trends in Cloud ERP is the increasing adoption of artificial intelligence (AI). AI can be used to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and provide insights into data. This can help businesses to improve their efficiency, productivity, and profitability.
Another major trend is the rise of cloud-native ERP solutions. Cloud-native ERP solutions are designed specifically for the cloud and take advantage of the cloud’s scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. This makes them a more attractive option for businesses than traditional on-premises ERP solutions.
Finally, there is a growing trend towards the adoption of industry-specific Cloud ERP solutions. Industry-specific Cloud ERP solutions are tailored to the specific needs of a particular industry, such as manufacturing, healthcare, or retail. This can help businesses to improve their efficiency and productivity by providing them with solutions that are designed to meet their specific needs.
Impact of Trends on the Future of Cloud ERP
The trends discussed above are having a significant impact on the future of Cloud ERP. They are making Cloud ERP solutions more affordable, easier to use, and more powerful than ever before. This is making Cloud ERP a more attractive option for businesses of all sizes.
In the future, we can expect to see even more innovation in the Cloud ERP market. AI, cloud-native solutions, and industry-specific solutions will continue to play a major role in shaping the future of Cloud ERP. Businesses that are looking to adopt a Cloud ERP solution should be aware of these trends and how they will impact their business.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Gartner Magic Quadrant for Cloud ERP is an invaluable resource for organizations considering a Cloud ERP implementation. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each vendor, organizations can make informed decisions that align with their specific business needs and drive digital transformation.
Originally posted 2024-05-20 16:07:00.
 Bussines News Daily
Bussines News Daily