The Gartner ERP Report stands as a beacon of industry insights, guiding organizations through the ever-evolving landscape of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solutions. This comprehensive report delves into key trends, vendor positioning, and best practices, empowering businesses to make informed decisions that drive operational excellence.
With its meticulous analysis and actionable recommendations, the Gartner ERP Report serves as an invaluable resource for businesses seeking to optimize their ERP strategies and stay ahead in today’s competitive market.
Market Overview
The Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) market is a rapidly evolving landscape, driven by technological advancements and the increasing demand for integrated business solutions. The market is characterized by a diverse range of vendors offering a wide spectrum of ERP solutions, catering to the specific needs of different industries and organizations.
Key trends shaping the ERP market include the rise of cloud-based ERP solutions, the adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies, and the growing emphasis on data analytics. These trends are driving innovation and enabling organizations to improve their operational efficiency, gain real-time insights into their businesses, and make informed decisions.
Major Players and Market Share
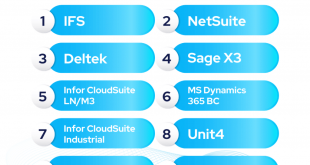
The ERP market is dominated by a few major players, including SAP, Oracle, Microsoft, and Infor. These vendors hold a significant market share and offer comprehensive ERP solutions that cater to a wide range of industries. However, there are also a number of smaller vendors that offer specialized ERP solutions for specific industries or niche markets.
The market share of major ERP vendors varies depending on the region and industry. In North America, SAP and Oracle are the leading vendors, while in Europe, SAP has a dominant market share. In the Asia-Pacific region, Oracle and SAP are the top players, while Infor has a strong presence in the Middle East and Africa.
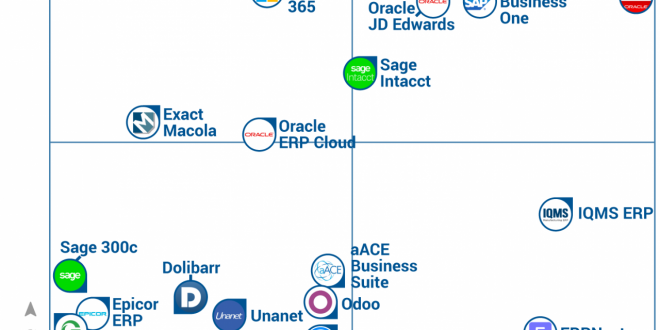
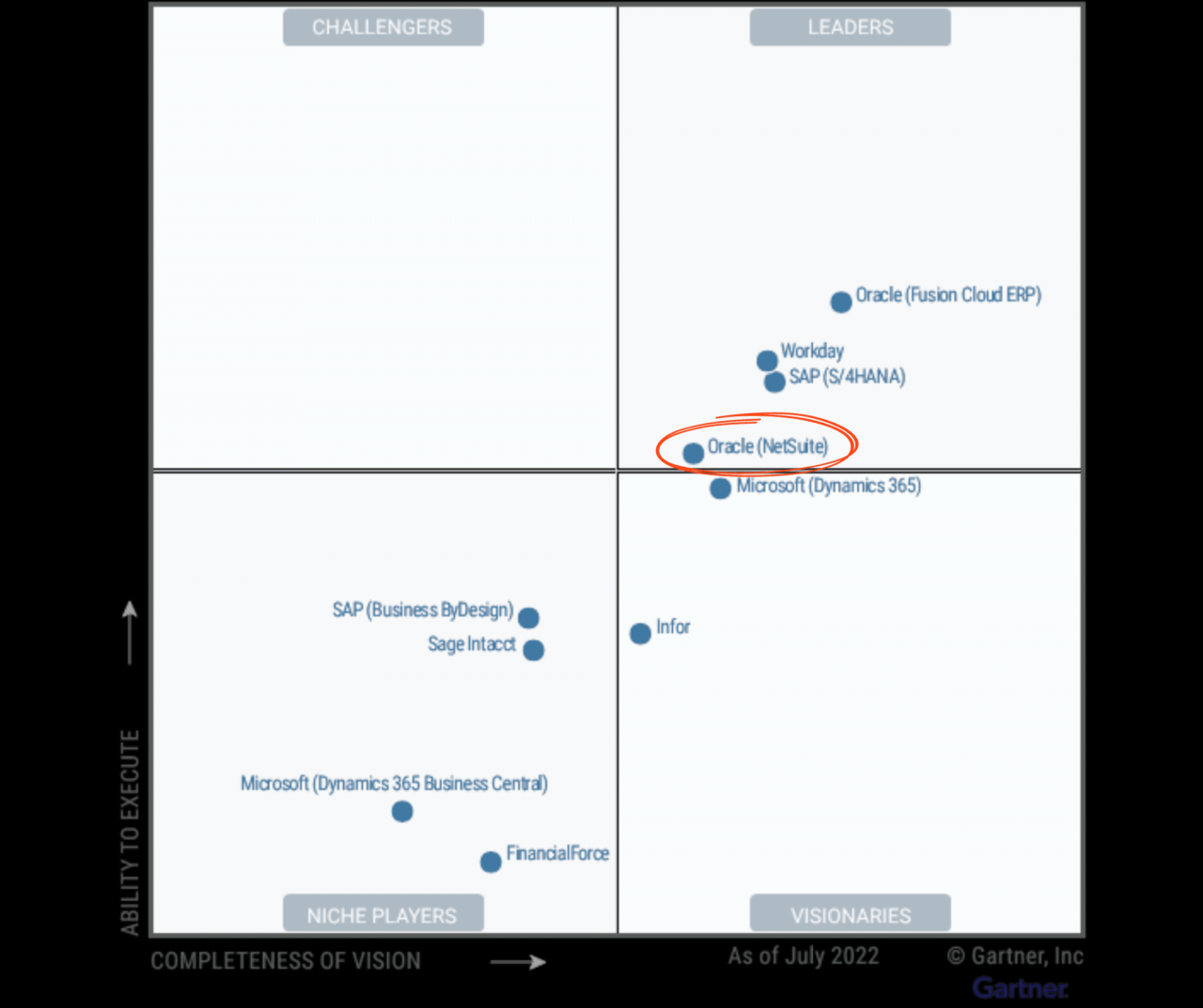
Gartner Magic Quadrant
The Gartner Magic Quadrant for ERP solutions is a widely recognized and respected tool for evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of vendors in the ERP market. Gartner analysts evaluate vendors based on two key criteria: completeness of vision and ability to execute.
Completeness of vision refers to a vendor’s understanding of the ERP market and its ability to articulate a clear and compelling vision for the future of ERP. Ability to execute refers to a vendor’s ability to deliver on its vision and execute its plans effectively.
Positioning of Vendors
The Magic Quadrant is divided into four quadrants:
- Leaders: These vendors have a strong vision and the ability to execute their plans. They are typically large, well-established vendors with a proven track record in the ERP market.
- Challengers: These vendors have a strong vision but may lack the ability to execute their plans. They may be smaller, newer vendors or vendors that are trying to enter the ERP market from another industry.
- Visionaries: These vendors have a strong vision but may lack the ability to execute their plans. They may be smaller, newer vendors or vendors that are trying to enter the ERP market from another industry.
- Niche Players: These vendors have a limited vision and may lack the ability to execute their plans. They may focus on a specific industry or a specific type of ERP solution.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Vendors
The Magic Quadrant also provides an analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of each vendor. This analysis can be used to help organizations select the right ERP vendor for their needs.
Some of the strengths and weaknesses that are typically considered include:
- Product functionality: The features and capabilities of the vendor’s ERP solution.
- Customer support: The level of support that the vendor provides to its customers.
- Implementation costs: The cost of implementing the vendor’s ERP solution.
- Total cost of ownership: The total cost of owning and operating the vendor’s ERP solution over its lifetime.
Key Findings and Recommendations
The Gartner ERP report provides valuable insights into the current state of the ERP market and offers recommendations for businesses looking to implement or optimize their ERP systems.
Key findings from the report include the growing adoption of cloud-based ERP solutions, the increasing importance of data and analytics, and the need for businesses to focus on user experience and integration.
Recommendations for Businesses
Based on these findings, Gartner recommends that businesses consider the following when evaluating or implementing an ERP system:
- Assess your business needs and requirements.What are the specific challenges you are trying to address with an ERP system? What are your goals for implementing an ERP system?
- Evaluate cloud-based ERP solutions.Cloud-based ERP solutions offer several benefits, including lower upfront costs, scalability, and flexibility.
- Focus on data and analytics.ERP systems can provide valuable data and insights that can help you make better decisions.
- Prioritize user experience.The ERP system should be easy to use and navigate for all users.
- Ensure integration with other systems.Your ERP system should be able to integrate with other systems, such as your CRM and accounting systems.
Best Practices for ERP Implementation and Optimization
In addition to the recommendations above, Gartner also provides best practices for ERP implementation and optimization:
- Get executive buy-in.ERP implementations are complex and require the support of senior management.
- Establish a clear project plan.Define the scope of the project, set timelines, and identify resources.
- Involve end-users in the implementation process.Get feedback from end-users throughout the implementation process to ensure that the system meets their needs.
- Test the system thoroughly.Before going live, test the system thoroughly to identify and resolve any issues.
- Provide ongoing training and support.Provide ongoing training and support to users to ensure that they are able to use the system effectively.
Industry Trends
The ERP market is constantly evolving, with new trends emerging all the time. These trends are having a major impact on businesses and their ERP strategies.
One of the most significant trends is the move towards cloud-based ERP systems. Cloud ERP systems are hosted by a third-party provider, which means that businesses can access their ERP system from anywhere with an internet connection. This is a major advantage for businesses that have multiple locations or that need to access their ERP system remotely.
Another major trend is the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) in ERP systems. AI can be used to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and provide insights into data. This can help businesses to improve their efficiency, productivity, and profitability.
Cloud-Based ERP Systems
- Benefits of cloud-based ERP systems:
- Increased flexibility and scalability
- Reduced IT costs
- Improved security
- Examples of businesses that are using cloud-based ERP systems:
- Coca-Cola
- General Electric
- Nike
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in ERP Systems
- Benefits of using AI in ERP systems:
- Automated tasks
- Improved decision-making
- Increased insights into data
- Examples of businesses that are using AI in ERP systems:
- Amazon
- Microsoft
These are just a few of the trends that are shaping the ERP market. Businesses that are able to adapt to these trends will be well-positioned to succeed in the future.
Case Studies
This section presents real-world examples of successful ERP implementations, highlighting the challenges and benefits experienced by these businesses. It offers insights into the factors that contributed to their success, providing valuable lessons for organizations considering ERP adoption.
Case Study: Manufacturing Company
A leading manufacturing company faced challenges in managing its complex supply chain and production processes. By implementing an ERP system, the company streamlined its operations, improved inventory management, and enhanced production efficiency. This resulted in significant cost savings, improved customer satisfaction, and increased profitability.
Case Study: Retail Enterprise
A large retail enterprise struggled with fragmented data and inefficient processes across its multiple locations. An ERP implementation integrated its operations, providing a single source of truth for inventory, sales, and customer information. This led to improved decision-making, reduced operational costs, and enhanced customer experiences.
Case Study: Healthcare Provider
A healthcare provider faced challenges in managing patient records, billing, and appointment scheduling. By implementing an ERP system, the provider improved patient care by streamlining medical records, automating billing processes, and enhancing appointment scheduling efficiency. This resulted in reduced errors, improved patient satisfaction, and increased revenue.
Competitive Landscape
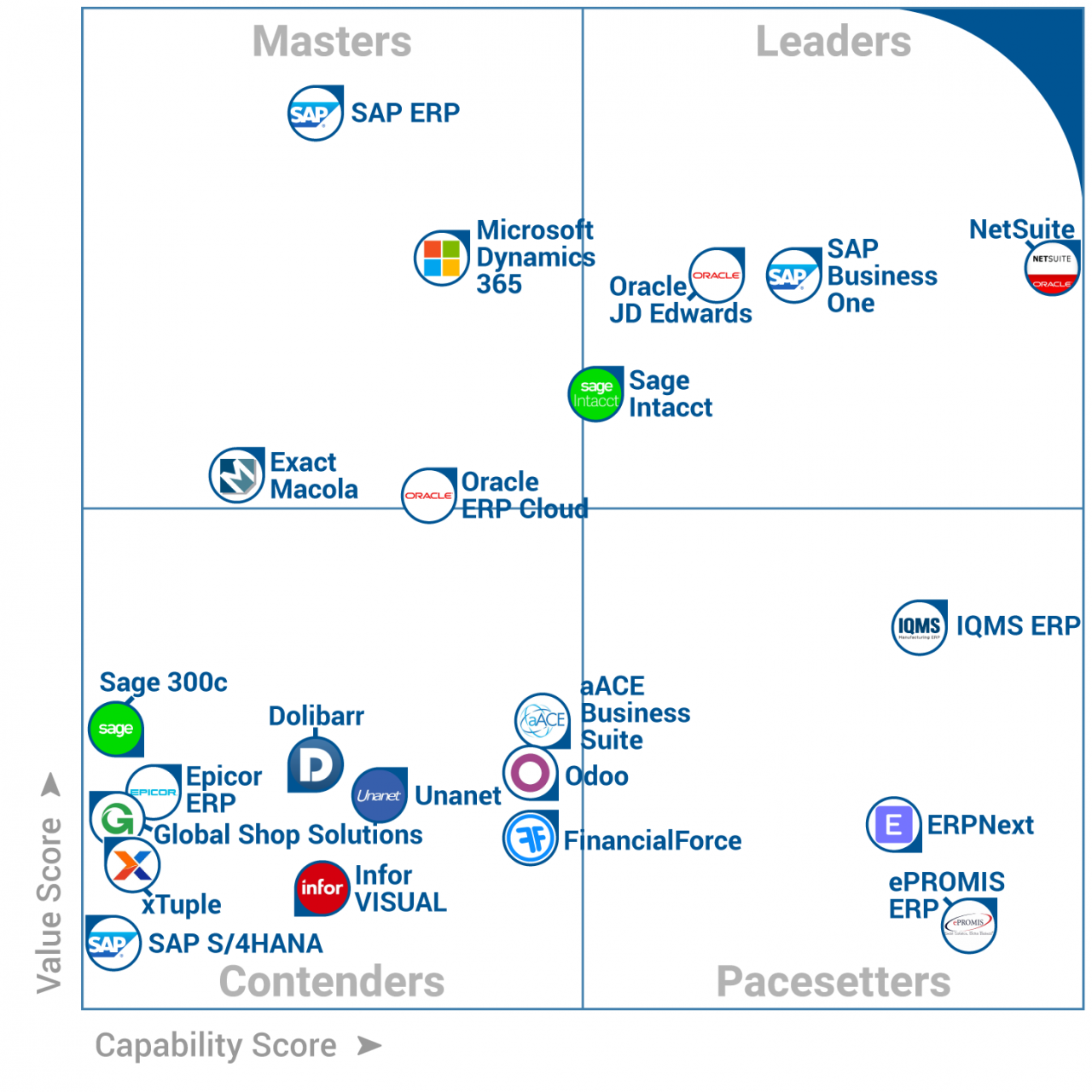
The ERP market is highly competitive, with numerous vendors offering a wide range of solutions. Each vendor has its own strengths and weaknesses, making it important for organizations to carefully evaluate their options before making a decision.
Some of the key players in the ERP market include SAP, Oracle, Microsoft, Infor, and Workday. These vendors offer a comprehensive suite of ERP applications that cover all aspects of business operations, from financial management to supply chain management.
Vendor Comparison, Gartner erp report
- SAP: SAP is the leading provider of ERP software, with a market share of over 25%. SAP’s ERP solutions are known for their scalability, flexibility, and integration capabilities.
- Oracle: Oracle is another major player in the ERP market, with a market share of around 20%. Oracle’s ERP solutions are known for their performance, reliability, and security.
- Microsoft: Microsoft is a relative newcomer to the ERP market, but has quickly gained market share with its Dynamics 365 ERP solution. Dynamics 365 is known for its ease of use, affordability, and integration with other Microsoft products.
- Infor: Infor is a leading provider of industry-specific ERP solutions. Infor’s ERP solutions are known for their depth of functionality and their ability to meet the specific needs of different industries.
- Workday: Workday is a cloud-based ERP provider that has gained popularity in recent years. Workday’s ERP solutions are known for their user-friendly interface, their scalability, and their ability to support global operations.
Areas of Differentiation
The different ERP vendors offer a variety of features and capabilities that can be used to differentiate their products. Some of the key areas of differentiation include:
- Functionality: The functionality of an ERP solution is one of the most important factors to consider when making a decision. Organizations should carefully evaluate the functionality of each solution to ensure that it meets their specific needs.
- Scalability: The scalability of an ERP solution is another important factor to consider. Organizations should choose a solution that can scale to meet their future growth needs.
- Flexibility: The flexibility of an ERP solution is also important. Organizations should choose a solution that can be easily customized to meet their specific needs.
- Integration: The ability of an ERP solution to integrate with other systems is also important. Organizations should choose a solution that can easily integrate with their existing systems, such as their CRM and financial systems.
- Cost: The cost of an ERP solution is also an important factor to consider. Organizations should choose a solution that fits within their budget.
Competitive Advantage
The competitive advantage of an ERP vendor is the unique set of features and capabilities that it offers. These features and capabilities can give the vendor an edge over its competitors.
Some of the key competitive advantages of the different ERP vendors include:
- SAP: SAP’s competitive advantage is its market leadership and its comprehensive suite of ERP solutions.
- Oracle: Oracle’s competitive advantage is its performance, reliability, and security.
- Microsoft: Microsoft’s competitive advantage is its ease of use, affordability, and integration with other Microsoft products.
- Infor: Infor’s competitive advantage is its depth of functionality and its ability to meet the specific needs of different industries.
- Workday: Workday’s competitive advantage is its user-friendly interface, its scalability, and its ability to support global operations.
Future Outlook
The future of the ERP market is expected to be shaped by several key trends, including the increasing adoption of cloud-based ERP solutions, the growing importance of data and analytics, and the emergence of new technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML).
Cloud-based ERP solutions offer several advantages over on-premise solutions, including lower costs, greater flexibility, and easier scalability. As a result, cloud-based ERP is expected to continue to gain market share in the coming years.
Data and analytics are becoming increasingly important for businesses of all sizes. ERP systems can provide businesses with valuable insights into their operations, which can help them to make better decisions and improve their performance.
AI and ML are two emerging technologies that have the potential to transform the ERP market. AI can be used to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and provide personalized recommendations. ML can be used to identify patterns and trends in data, which can help businesses to make better predictions and decisions.
Potential Growth Areas
Some of the potential growth areas in the ERP market include:
- Cloud-based ERP
- Data and analytics
- AI and ML
- Vertical-specific ERP solutions
- ERP for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs)
How Businesses Can Prepare for the Future of ERP
Businesses can prepare for the future of ERP by taking the following steps:
- Evaluate their current ERP system and identify areas for improvement.
- Consider cloud-based ERP solutions as a way to reduce costs and increase flexibility.
- Invest in data and analytics to gain valuable insights into their operations.
- Explore the potential of AI and ML to automate tasks and improve decision-making.
- Partner with an ERP vendor that has a strong track record of innovation and customer support.
End of Discussion: Gartner Erp Report
In conclusion, the Gartner ERP Report provides a roadmap for businesses to navigate the complexities of the ERP market and make strategic decisions that align with their unique needs. By leveraging the insights and recommendations contained within this report, organizations can harness the power of ERP solutions to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and gain a competitive edge in the digital age.
Originally posted 2024-05-20 10:54:32.
 Bussines News Daily
Bussines News Daily