As ERP software tools take center stage, they have revolutionized the way businesses operate. These comprehensive solutions seamlessly integrate various aspects of an organization, enabling enhanced efficiency, informed decision-making, and a competitive edge in today’s dynamic market landscape.
With their robust features and customizable capabilities, ERP software tools have become indispensable for businesses seeking to streamline their operations, optimize resources, and achieve sustainable growth.
ERP Software Tools Overview
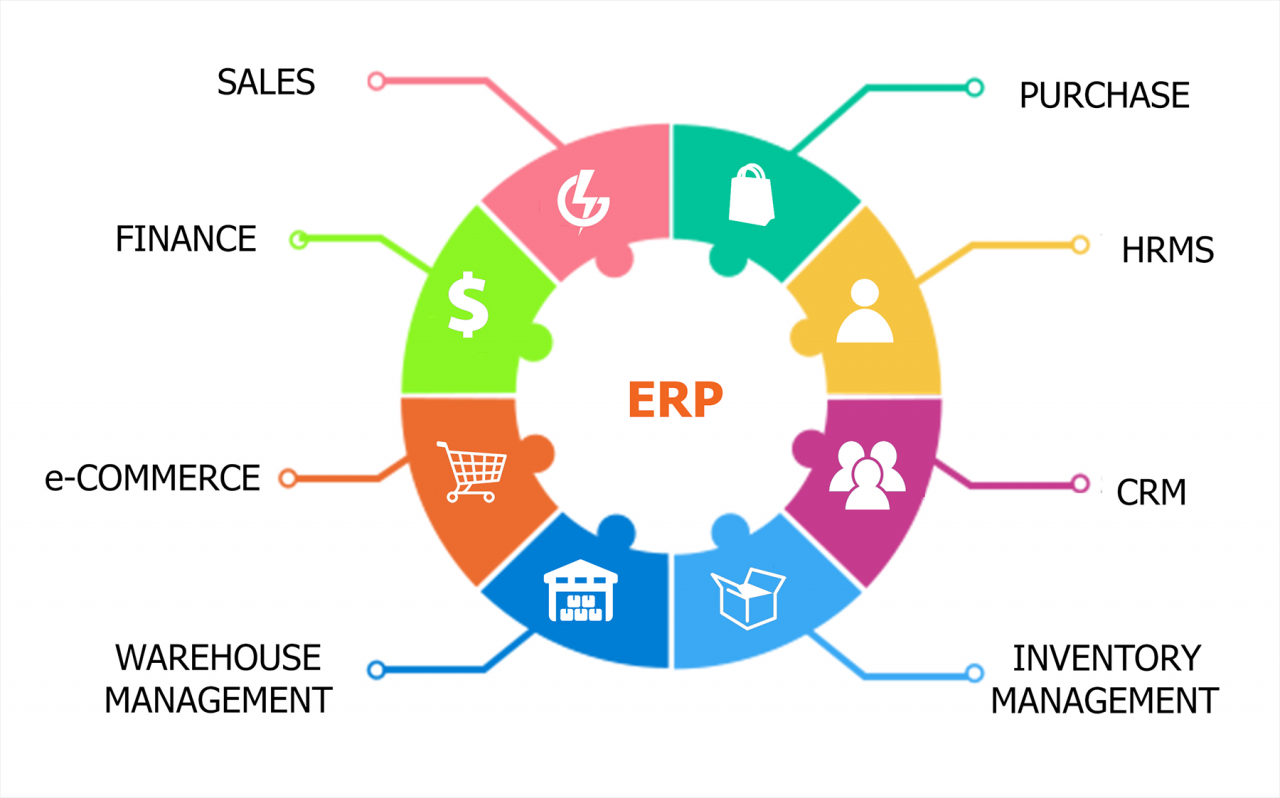
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software tools are comprehensive business management systems that integrate and automate various core business processes across an organization.
Key functions of ERP software include:
- Financial management
- Human resources management
- Supply chain management
- Customer relationship management
- Manufacturing
Benefits of ERP Software
ERP software offers several benefits, including:
- Improved efficiency and productivity
- Reduced costs
- Enhanced data accuracy and consistency
- Increased collaboration and communication
- Better decision-making
Limitations of ERP Software
ERP software also has some limitations, such as:
- High implementation and maintenance costs
- Complexity and potential for user resistance
- Difficulty in integrating with legacy systems
Common ERP Software Tools in the Market
Some common ERP software tools in the market include:
- SAP
- Oracle NetSuite
- Microsoft Dynamics 365
- Sage Intacct
- Epicor
Key Features of ERP Software Tools
ERP software tools offer a comprehensive suite of features that streamline business processes, enhance collaboration, and provide real-time insights. These features are essential for businesses looking to improve efficiency, optimize decision-making, and gain a competitive edge.
Integration, automation, and real-time data access are the cornerstones of ERP software tools. Integration allows different departments and systems to share data seamlessly, eliminating silos and improving communication. Automation streamlines repetitive tasks, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic initiatives.
Real-time data access provides up-to-date information, enabling businesses to make informed decisions based on the latest available data.
Integration
- Connects different departments and systems within an organization.
- Eliminates data silos and improves communication.
- Provides a single source of truth for all business data.
Automation
- Streamlines repetitive tasks, such as data entry and invoice processing.
- Frees up employees to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Reduces errors and improves efficiency.
Real-Time Data Access
- Provides up-to-date information on all aspects of the business.
- Enables businesses to make informed decisions based on the latest available data.
- Improves responsiveness to changing market conditions.
Types of ERP Software Tools
ERP software tools can be categorized based on their deployment type, which determines how they are accessed and managed. The three main deployment types are on-premise, cloud, and hybrid.
Each deployment type offers distinct advantages and disadvantages, making it suitable for different organizations depending on their specific requirements and infrastructure.
On-Premise ERP Software Tools
- Advantages:
- Greater control over data and security
- Customization and flexibility to meet specific business needs
- Potential cost savings in the long run
- Disadvantages:
- Higher upfront investment in hardware, software, and IT staff
- Ongoing maintenance and support costs
- Limited scalability and agility
Examples:SAP S/4HANA, Oracle E-Business Suite, Microsoft Dynamics AX
Cloud ERP Software Tools
- Advantages:
- Lower upfront costs and ongoing expenses
- Scalability and flexibility to meet changing business needs
- Automatic updates and maintenance
- Disadvantages:
- Less control over data and security
- Customization and integration challenges
- Reliance on internet connectivity
Examples:Salesforce, NetSuite, SAP Business ByDesign
Hybrid ERP Software Tools
- Advantages:
- Combines the benefits of both on-premise and cloud deployment
- Flexibility to deploy specific modules or functions on-premise or in the cloud
- Improved data security and control
- Disadvantages:
- Can be more complex to implement and manage
- Potential compatibility issues between on-premise and cloud components
Examples:Oracle Cloud ERP, Microsoft Dynamics 365, Infor CloudSuite Industrial
ERP Software Implementation

ERP software implementation is a complex process that requires careful planning and execution. The key steps involved in ERP software implementation include:
- Planning:This involves defining the project scope, timeline, and budget, as well as identifying the resources that will be needed.
- Change management:This is essential to ensure that the organization is prepared for the changes that ERP software will bring. It involves communicating with employees, training them on the new system, and providing support during the transition.
- Data migration:This involves moving data from the old system to the new ERP system. It is important to ensure that the data is accurate and complete, and that it is migrated in a way that minimizes disruption to the business.
- Testing:This is essential to ensure that the ERP system is working properly before it is put into production. It involves testing the system with real-world data and scenarios.
- Deployment:This involves rolling out the ERP system to the organization. It is important to do this in a phased approach, so that the organization can adapt to the new system gradually.
- Support:This is essential to ensure that the ERP system is running smoothly and that users are getting the support they need. It involves providing training, documentation, and technical support.
Following these best practices can help organizations successfully implement ERP software:
- Get buy-in from top management:This is essential to ensure that the project has the necessary resources and support.
- Create a detailed implementation plan:This will help to keep the project on track and avoid surprises.
- Communicate with employees regularly:This will help to keep them informed about the project and to reduce resistance to change.
- Train employees thoroughly:This will help them to get up to speed on the new system quickly and to use it effectively.
- Test the system thoroughly:This will help to identify and fix any problems before the system is put into production.
- Deploy the system in a phased approach:This will help to minimize disruption to the business.
- Provide ongoing support:This will help to ensure that the system is running smoothly and that users are getting the support they need.
ERP Software Integration
ERP software integration is crucial for businesses seeking to streamline their operations and enhance data accuracy. It allows ERP systems to seamlessly exchange information with other business applications, eliminating manual data entry and reducing errors.
There are several methods for integrating ERP software with other systems, including:
API Integration
API (Application Programming Interface) integration involves creating a direct connection between the ERP system and other applications. This allows for real-time data exchange and eliminates the need for manual data transfer.
Middleware Integration, Erp software tools
Middleware is a software layer that acts as an intermediary between the ERP system and other applications. It facilitates data translation and transformation, ensuring seamless communication between different systems.
Examples of Successful ERP Software Integration Projects
- A manufacturing company integrated its ERP system with a CRM system, enabling real-time visibility into customer orders and inventory levels.
- A retail chain integrated its ERP system with a point-of-sale (POS) system, automating the sales process and improving inventory management.
- A healthcare organization integrated its ERP system with a patient management system, streamlining patient records and enhancing care coordination.
ERP Software Customization
ERP software customization is crucial to adapt the system to meet the unique requirements of specific businesses. It allows organizations to tailor the software to align with their industry-specific processes, workflows, and reporting needs.
Approaches to ERP Software Customization
There are several approaches to ERP software customization, including:
- Add-ons:Pre-built modules or extensions that can be integrated with the ERP system to add specific functionality.
- Extensions:Custom-developed code that extends the core functionality of the ERP system to meet specific requirements.
- Configuration:Modifying the system’s parameters and settings to align with the business’s processes without altering the core code.
Case Studies of Successful ERP Software Customization Projects
Numerous organizations have successfully implemented customized ERP software solutions. Here are a few case studies:
- Manufacturing Company:A manufacturing company customized its ERP system to streamline its production processes, reducing lead times and improving efficiency.
- Retail Chain:A retail chain customized its ERP system to integrate with its e-commerce platform, providing real-time inventory visibility and improving customer satisfaction.
- Healthcare Provider:A healthcare provider customized its ERP system to manage patient records, automate billing processes, and improve communication among different departments.
ERP Software Trends
ERP software technology is constantly evolving, with new trends emerging all the time. Some of the most important trends include the adoption of cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML).
Cloud computing allows businesses to access ERP software applications over the internet, rather than having to install and maintain the software on their own servers. This can save businesses money and time, and it can also make it easier to scale their ERP systems as their business grows.
AI and ML are being used to automate many of the tasks that are traditionally performed by ERP software. This can free up employees to focus on more strategic tasks, and it can also help businesses to improve the efficiency of their ERP systems.
The Future of ERP Software Tools
The future of ERP software tools is bright. As cloud computing, AI, and ML continue to develop, ERP software will become even more powerful and easier to use. This will make ERP software even more essential for businesses of all sizes.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, ERP software tools have emerged as a cornerstone of modern business operations, offering a transformative solution to enhance efficiency, foster collaboration, and drive informed decision-making. As technology continues to evolve, the future of ERP software holds immense promise, with advancements such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and machine learning poised to further revolutionize the way businesses operate.
Originally posted 2024-05-20 11:45:16.
 Bussines News Daily
Bussines News Daily