Erp software gartner magic quadrant – The Gartner Magic Quadrant for ERP Software is a highly respected and influential report that evaluates the leading vendors in the ERP software market. This comprehensive analysis provides valuable insights into the strengths, weaknesses, and market positions of the top ERP software providers, helping businesses make informed decisions about their ERP software investments.
The Gartner Magic Quadrant methodology is based on a rigorous evaluation process that considers a wide range of factors, including functionality, innovation, customer satisfaction, and market share. By analyzing these key dimensions, Gartner provides a clear and objective assessment of the ERP software market landscape.
ERP Software Market Overview
The global ERP software market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing adoption of digital technologies and the need for businesses to streamline their operations. The market is expected to reach a value of $56.2 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 10.5% from 2021 to 2026.
Key industry players include SAP, Oracle, Microsoft, Infor, and NetSuite. These companies offer a wide range of ERP solutions that cater to the needs of businesses of all sizes and industries. The competitive landscape is characterized by intense competition, with each vendor focusing on innovation and differentiation to gain market share.
Market Dynamics
The ERP software market is influenced by several key dynamics, including:
- Cloud adoption:The increasing adoption of cloud-based ERP solutions is a major trend in the market. Cloud ERP offers businesses greater flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
- Artificial intelligence (AI):AI is playing an increasingly important role in ERP systems. AI-powered ERP solutions can automate tasks, improve decision-making, and provide insights into business data.
- Integration with other systems:ERP systems need to integrate with other business systems, such as CRM, SCM, and HCM. Seamless integration is essential for businesses to achieve a unified view of their operations.
Gartner Magic Quadrant Analysis
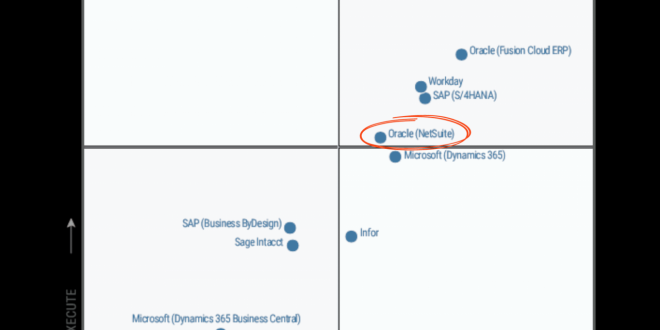
The Gartner Magic Quadrant is a graphical representation of the market for a particular technology or service. It positions vendors based on their ability to execute and completeness of vision.
Gartner uses a rigorous methodology to evaluate ERP software vendors. The methodology includes a detailed questionnaire, customer reference checks, and a financial analysis. The questionnaire covers a wide range of topics, including product functionality, customer support, and financial stability.
Key Dimensions and Metrics
The Magic Quadrant is based on two key dimensions: ability to execute and completeness of vision. Ability to execute measures a vendor’s ability to deliver on its promises. Completeness of vision measures a vendor’s understanding of the market and its ability to innovate.
Gartner also considers a number of other metrics when evaluating ERP software vendors. These metrics include:
- Market share
- Customer satisfaction
- Financial performance
- Product roadmap
- Innovation
Quadrant Leaders
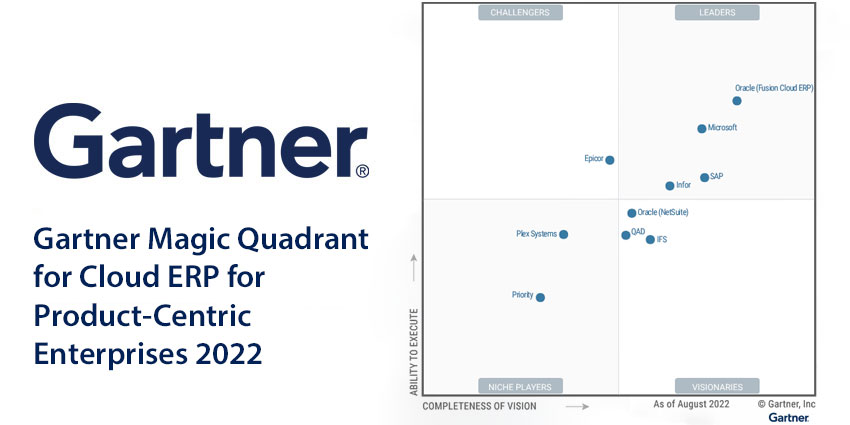
The Leaders quadrant in Gartner’s Magic Quadrant for ERP Software represents vendors who have established a strong presence in the market, with comprehensive product offerings, proven innovation capabilities, and high customer satisfaction. These vendors are widely recognized for their ability to deliver value to their customers and drive business transformation.
Key characteristics of Quadrant Leaders include:
- Strong market share and brand recognition
- Comprehensive product portfolio covering a wide range of ERP functionalities
- Proven track record of innovation and technology leadership
- High customer satisfaction and positive feedback from industry analysts
- Strong financial performance and a commitment to ongoing investment in research and development
Let’s explore some of the key Quadrant Leaders and their strengths:
SAP
- Core strengths: SAP is known for its comprehensive ERP suite, SAP S/4HANA, which offers a wide range of modules covering all aspects of business operations. The company has a strong global presence and a large customer base, particularly in large enterprises.
- Weaknesses: SAP’s products can be complex and expensive to implement, and the company has been criticized for its slow pace of innovation in recent years.
- Market share: SAP is the market leader in ERP software, with a significant market share globally.
Oracle
- Core strengths: Oracle’s ERP offering, Oracle Fusion Cloud ERP, is known for its scalability, flexibility, and ease of use. The company has a strong presence in the cloud ERP market and offers a wide range of industry-specific solutions.
- Weaknesses: Oracle’s products can be expensive, and the company has been criticized for its aggressive sales tactics.
- Market share: Oracle is a major player in the ERP market, with a significant market share globally.
Microsoft
- Core strengths: Microsoft’s ERP offering, Dynamics 365, is known for its integration with other Microsoft products and its ease of use. The company has a strong presence in the mid-market and small business segments.
- Weaknesses: Microsoft’s ERP offering may not be as comprehensive as some of its competitors, and the company has been criticized for its lack of industry-specific expertise.
- Market share: Microsoft is a growing player in the ERP market, with a significant market share in the mid-market and small business segments.
Challengers and Visionaries: Erp Software Gartner Magic Quadrant
The Challengers and Visionaries quadrants in Gartner’s Magic Quadrant for ERP Software encompass vendors with a strong presence and potential for growth. Challengers possess the capabilities to compete with Leaders, while Visionaries exhibit innovative approaches and a clear vision for the future of ERP.
These vendors have the potential to move up the rankings by leveraging their strengths and addressing areas for improvement. They can challenge the Leaders by offering differentiated solutions, expanding their market reach, and investing in technological advancements.
Growth Strategies
- Expanding into new markets and industries
- Acquiring complementary solutions and technologies
- Developing strategic partnerships and alliances
- Focusing on customer retention and upselling
Technological Advancements
- Incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML)
- Developing cloud-based ERP solutions
- Enhancing user experience and mobile functionality
- Investing in research and development (R&D)
Market Differentiation
- Offering industry-specific solutions
- Targeting specific customer segments
- Developing unique value propositions
- Providing exceptional customer support
Niche Players
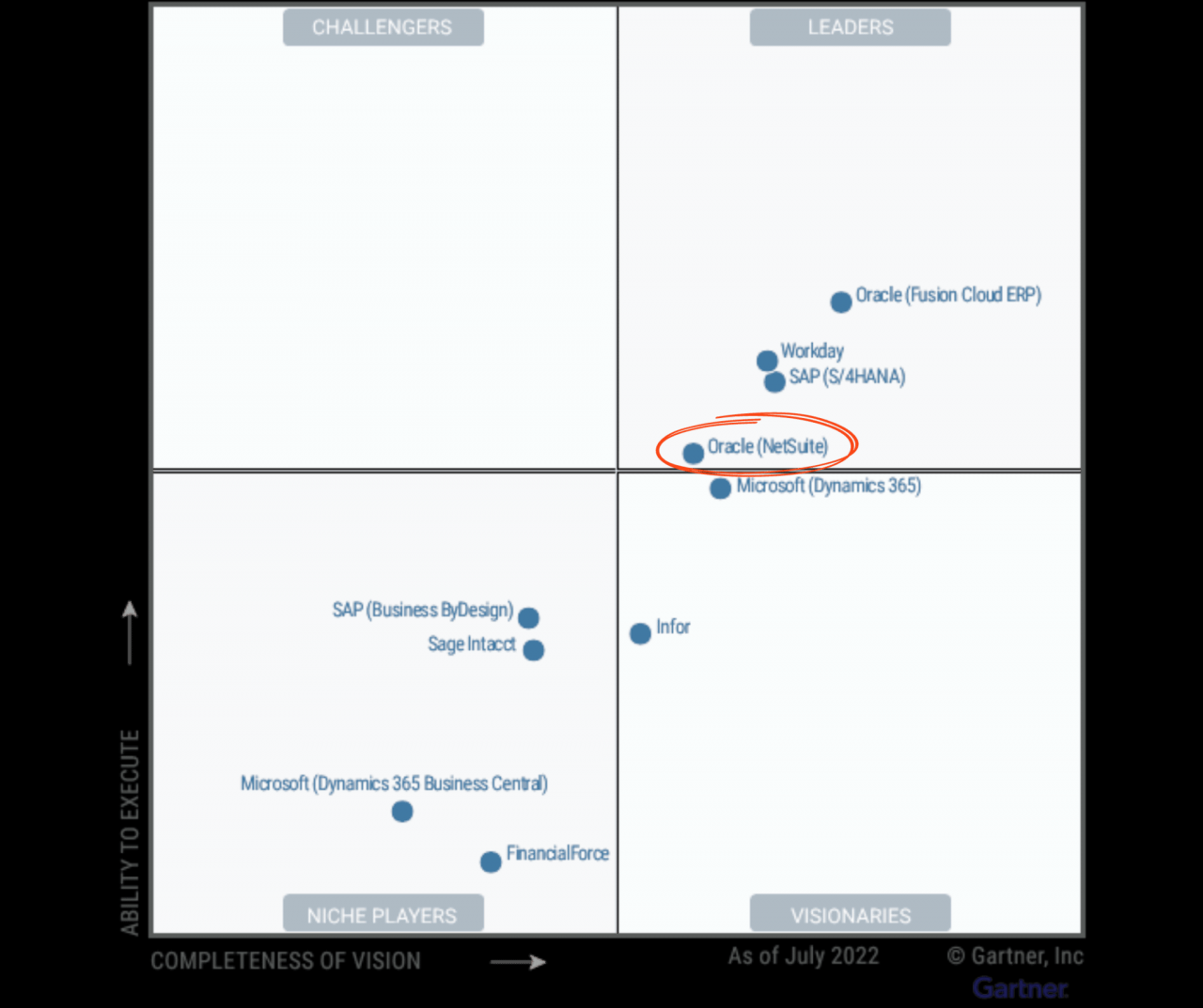
Niche Players in the Gartner Magic Quadrant for ERP Software are vendors that focus on specific industries or market segments. They have a deep understanding of the unique requirements of their target market and offer specialized solutions that meet those needs.
Niche Players typically have a smaller market share than the leaders and challengers, but they can be very successful by focusing on a specific area and developing a strong reputation for excellence in that area.
Competitive Advantages
Niche Players often have a number of competitive advantages over the larger vendors, including:
- Deep industry knowledge:Niche Players have a deep understanding of the unique requirements of their target market. This allows them to develop solutions that are specifically tailored to the needs of their customers.
- Specialized solutions:Niche Players offer specialized solutions that are designed to meet the specific needs of their target market. These solutions are often more comprehensive and feature-rich than the general-purpose solutions offered by the larger vendors.
- Strong customer relationships:Niche Players typically have strong customer relationships. They understand the needs of their customers and are committed to providing them with the best possible service.
Growth Opportunities
Niche Players have a number of growth opportunities, including:
- Expansion into new markets:Niche Players can expand their market share by expanding into new markets. This can be done by targeting new industries or by developing new solutions for their existing target market.
- Product innovation:Niche Players can also grow by innovating their products. This can be done by adding new features or by developing new solutions that meet the changing needs of their customers.
- Acquisitions:Niche Players can also grow by acquiring other companies. This can be a good way to expand their product portfolio or to enter new markets.
ERP Software Selection Considerations
Selecting the right ERP software solution is critical for businesses looking to streamline their operations and improve efficiency. Several key factors should be considered when making this decision.
The following table summarizes the key factors to consider when selecting an ERP software solution:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Functionality | The software’s ability to meet the specific needs and requirements of the business. |
| Scalability | The software’s ability to handle the growing needs of the business as it expands. |
| Cost | The total cost of ownership, including the purchase price, implementation costs, and ongoing maintenance fees. |
| Implementation Complexity | The difficulty and time required to implement the software. |
| Vendor Support | The quality and responsiveness of the vendor’s support team. |
By carefully considering these factors, businesses can make an informed decision that will help them select the best ERP software solution for their needs.
Case Studies and Best Practices
Organizations that have successfully implemented ERP software often share their experiences through case studies. These case studies provide valuable insights into the challenges faced, lessons learned, and best practices adopted during the implementation process.
By examining these case studies, organizations can gain a better understanding of the potential benefits and pitfalls of ERP software implementation. They can also learn from the experiences of others and identify strategies to improve their own implementation efforts.
Benefits of ERP Software Implementation, Erp software gartner magic quadrant
- Improved efficiency and productivity
- Reduced costs
- Enhanced customer satisfaction
- Increased collaboration and communication
- Improved decision-making
Outcome Summary
The Gartner Magic Quadrant for ERP Software is an essential resource for businesses looking to select and implement an ERP software solution. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of the leading vendors, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their specific needs and goals.
The report also provides valuable insights into the future of the ERP software market, helping businesses stay ahead of the curve and make strategic decisions that will drive long-term success.
Originally posted 2024-05-20 10:44:47.
 Bussines News Daily
Bussines News Daily