Cloud web security takes center stage in this discourse, inviting you to delve into a narrative meticulously crafted with precision and eloquence. Its significance in safeguarding web applications and data in the cloud cannot be overstated, and this discourse will illuminate its intricacies with clarity and depth.
As we navigate this digital landscape, the prevalence of web attacks in the cloud looms large. Statistics and case studies will be presented to underscore the magnitude of these threats and their potential impact on businesses and organizations.
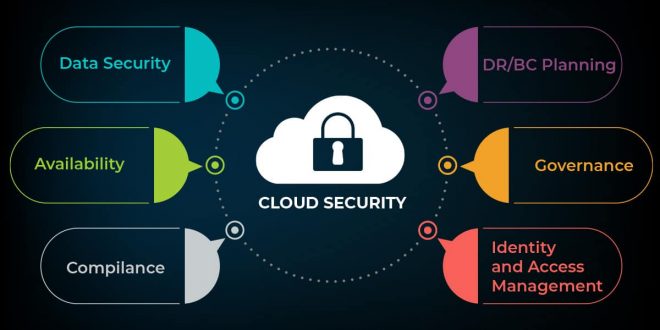
Overview of Cloud Web Security
Cloud web security encompasses a set of technologies and practices designed to protect web applications and data hosted in the cloud from various cyber threats. It has gained significant importance due to the increasing adoption of cloud computing, which introduces new security challenges.
Web attacks in the cloud have become prevalent, with numerous high-profile incidents reported in recent years. Statistics indicate that web application attacks account for a significant portion of data breaches, resulting in substantial financial losses and reputational damage for organizations.
Prevalence of Web Attacks in the Cloud
- According to a report by Verizon, web application attacks were the most common type of cyberattack in 2021, accounting for 43% of all breaches.
- A study by IBM found that cloud-based web applications are 60% more likely to be targeted by attacks compared to on-premises applications.
- The Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) reported that web attacks in the cloud are becoming increasingly sophisticated, with attackers using advanced techniques such as zero-day exploits and social engineering.
Types of Cloud Web Security Threats
Cloud environments present unique security challenges due to their distributed nature and reliance on shared resources. Attackers exploit various vulnerabilities to compromise cloud-based web applications and data.
Common Web Attacks Targeting Cloud Environments, Cloud web security
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks:Attackers overwhelm cloud servers with a flood of traffic, causing websites and applications to become inaccessible.
- SQL Injection Attacks:Attackers exploit vulnerabilities in database queries to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data or execute malicious commands.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Attacks:Attackers inject malicious scripts into web pages, allowing them to steal user credentials, redirect traffic, or compromise other websites.
- Phishing Attacks:Attackers create fake websites or emails that mimic legitimate ones to trick users into providing sensitive information, such as passwords or credit card numbers.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks:Attackers intercept communications between users and web applications, allowing them to eavesdrop on traffic or modify data.
Cloud Web Security Best Practices
Securing cloud web applications is crucial to protect against malicious attacks and data breaches. Implementing robust security measures is essential for maintaining the integrity and availability of web applications hosted in the cloud.
Here are some best practices to enhance cloud web security:
Implementing Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems
- Firewalls act as a barrier between the internet and your cloud environment, blocking unauthorized access and malicious traffic.
- Intrusion detection systems (IDS) monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and alert administrators to potential threats.
Using Web Application Firewalls (WAFs)
- WAFs are specialized firewalls designed to protect web applications from common attacks such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS).
- They monitor incoming traffic and block requests that match predefined security rules.
Enforcing Secure Coding Practices
- Secure coding practices involve writing code that is resistant to vulnerabilities and exploits.
- Developers should follow secure coding guidelines and use security libraries to prevent common coding errors.
Regularly Patching and Updating Software
- Software vulnerabilities can provide attackers with entry points into your system.
- Regularly patching and updating software, including the operating system, web server, and application software, is essential to address vulnerabilities and improve security.
Cloud Web Security Tools and Technologies
Various tools and technologies can enhance cloud web security, including:
Security Scanners
Security scanners automatically examine websites and web applications for vulnerabilities, such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting. They can help identify potential security risks and provide recommendations for remediation.
Penetration Testing Tools
Penetration testing tools simulate attacks on web applications to identify exploitable vulnerabilities. They can help organizations assess the effectiveness of their security measures and identify areas for improvement.
Cloud Security Platforms
Cloud security platforms offer a comprehensive suite of security tools and services tailored for cloud environments. They can provide centralized visibility and control over cloud resources, enabling organizations to monitor security events, detect threats, and respond quickly to incidents.
Cloud Web Security Compliance and Regulations
Cloud web security compliance involves adhering to industry standards and regulations to ensure the protection of sensitive data and systems. Understanding and complying with these regulations is crucial for organizations to maintain data security, avoid penalties, and build trust with customers.
PCI DSS
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) is a set of security standards developed by the payment card industry to protect cardholder data. It applies to organizations that process, store, or transmit payment card data. Compliance with PCI DSS involves implementing technical and operational controls to safeguard cardholder data, such as encryption, access controls, and regular security assessments.
HIPAA
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) is a US regulation that sets standards for protecting the privacy and security of health information. Healthcare organizations and their business associates must comply with HIPAA to safeguard patient data. Compliance involves implementing technical, physical, and administrative safeguards, including encryption, access controls, and data breach notification procedures.
GDPR
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) is a European Union regulation that protects the personal data of EU citizens. It applies to organizations that process or hold personal data of EU citizens, regardless of their location. Compliance with GDPR involves implementing measures to ensure data privacy, including obtaining consent for data processing, providing data subject rights, and implementing data breach notification procedures.Ensuring
compliance with these regulations involves conducting risk assessments, implementing appropriate security controls, and regularly monitoring and auditing systems. Organizations should also stay updated on the latest regulatory changes and industry best practices to maintain compliance and protect their cloud web assets.
Emerging Trends in Cloud Web Security
Cloud web security continues to evolve, with new trends and advancements emerging all the time. These trends are being driven by the increasing adoption of cloud computing, the growing sophistication of cyber threats, and the need for businesses to protect their data and applications in the cloud.
Some of the most important emerging trends in cloud web security include:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) for Threat Detection
AI and ML are being used to develop new and more effective ways to detect threats in the cloud. These technologies can be used to analyze large volumes of data in real time, identify patterns, and predict threats before they can cause damage.
AI and ML can also be used to automate threat detection and response, making it faster and more efficient.
Serverless Security
Serverless computing is a cloud computing model in which the cloud provider manages the servers and infrastructure, allowing developers to focus on writing code. This model can help to improve security by reducing the attack surface and eliminating the need for businesses to manage and patch servers.
Serverless security solutions are designed to protect serverless applications from threats such as injection attacks, cross-site scripting (XSS), and denial of service (DoS) attacks.
Cloud-Native Application Protection Platforms (CNAPPs)
CNAPPs are a new type of security solution that is designed to protect cloud-native applications. These solutions provide a comprehensive set of security features, including threat detection, vulnerability management, and compliance monitoring. CNAPPs can help businesses to improve the security of their cloud-native applications and reduce the risk of data breaches.
Case Studies and Examples

Real-world case studies and examples showcase the successful implementation of cloud web security measures. These case studies highlight the challenges encountered and lessons learned, providing valuable insights into effective cloud web security practices.
Case Study: Securing a Global E-commerce Platform
A leading e-commerce company faced challenges securing its rapidly growing cloud-based platform. By implementing a comprehensive cloud web security solution, including a web application firewall, intrusion detection system, and vulnerability management tools, they significantly reduced the risk of data breaches and malicious attacks.
Case Study: Protecting a Cloud-Based Healthcare System
A healthcare provider migrated its patient data and applications to a cloud environment. To ensure the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive patient information, they implemented a multi-layered cloud web security approach that included encryption, access control, and regular security audits.
Lessons Learned
- Proactive security measures are essential to prevent attacks and data breaches.
- Collaboration between security and development teams is crucial for effective cloud web security.
- Regular security audits and testing help identify and address vulnerabilities.
Epilogue

In conclusion, cloud web security emerges as a cornerstone of digital protection, empowering organizations to navigate the complexities of the cloud with confidence. By embracing best practices, leveraging advanced tools and technologies, and adhering to compliance standards, businesses can fortify their web applications and data against evolving threats.
As the digital realm continues to expand, cloud web security will remain an indispensable ally in safeguarding our online presence.
 Bussines News Daily
Bussines News Daily